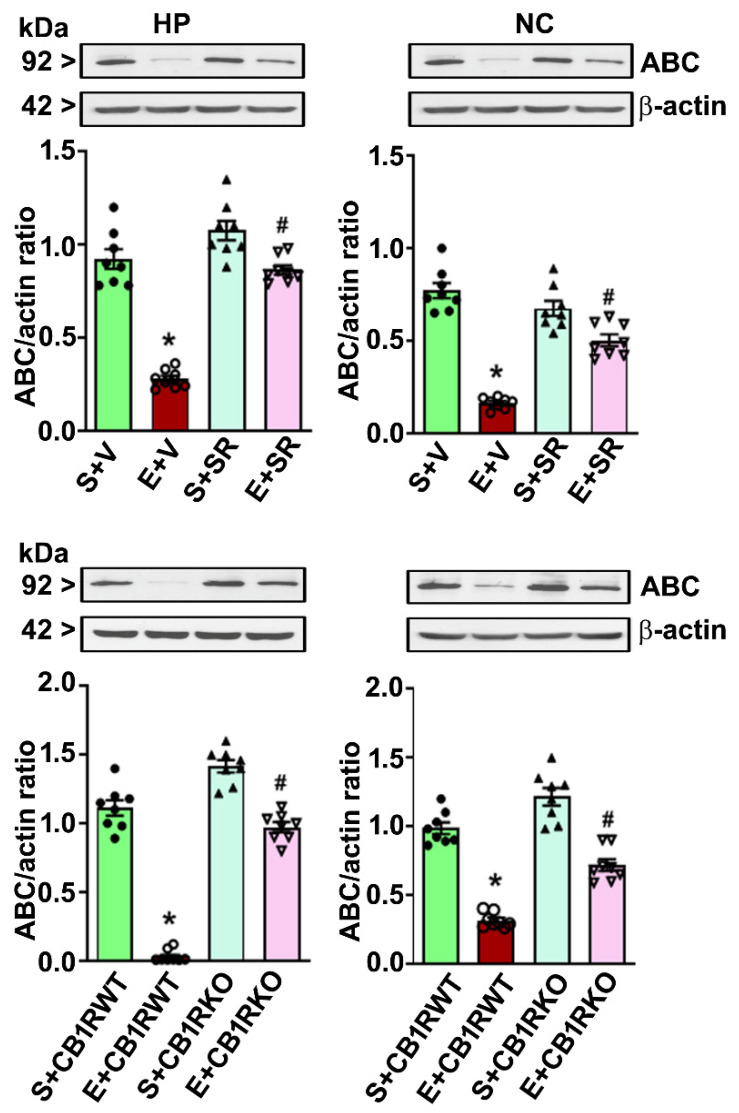
Figure 5.
Pharmacological inhibition or genetic deletion of CB1Rs mitigates the loss of nuclear ABC caused by high-dose ethanol exposure in P7 mice. The ABC protein levels were evaluated by Western blot analysis in the nuclear fractions of the HP and NC samples from the different treatment groups (S + V, E + V, S + SR and E + SR; S + CB1RWT, E + CB1RWT, S + CB1RKO and E + CB1RKO). Error bars, SEM (* p < 0.05 vs. the S + V or CB1RWT + S group; # p < 0.05 vs. the E + V or CB1RWT + E group, n = 8 pups/group).