Figure 2.
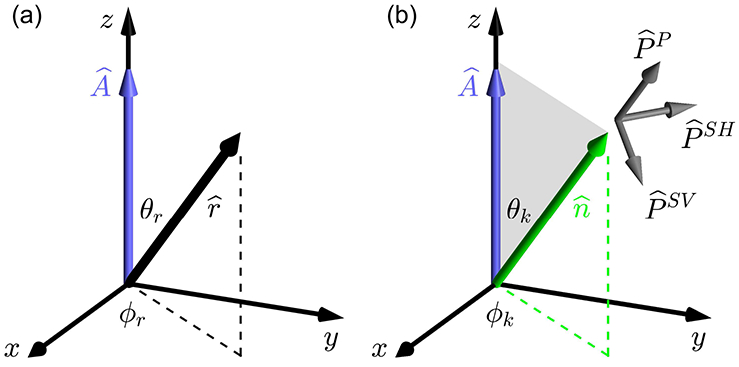
Coordinate system with x, y, and z axes used for the analysis of the material, wave propagation, and Green’s tensor in Sections 2 and 3. This coordinate system is distinct from the experimental XYZ coordinate system in figure 1. The relation between the xyz and XYZ coordinate systems is described in Section 4.2. (a) The xyz coordinate system is oriented so that the z axis is aligned with the material symmetry axis , and the position vector is specified by the angles θr and ϕr. To simplify the analysis in Section 3.1, the axes are rotated so that ϕr = 0. (b) Wave propagation is in the direction with wave vector = k at an angle θk relative to the material symmetry axis . The polarization vectors are defined relative to the − plane shown in gray with the SH polarization perpendicular to the − plane, and the SV and P polarizations in the − plane. Explicit expressions for polarization vectors are given in terms of θk and ϕk in (24).
