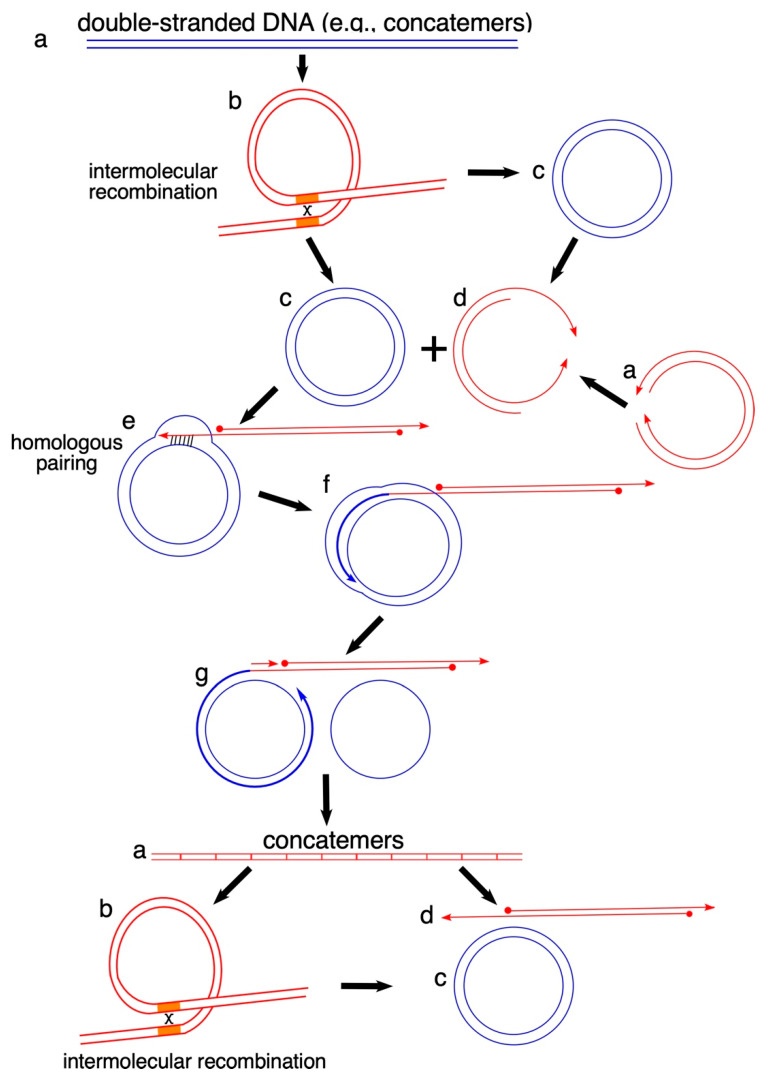
Figure 1.
Homologous pairing–mediated mtDNA replication via a rolling-circle mechanism. mtDNA replication is initiated from double-stranded DNA, such as a concatemer (a). Intramolecular recombination (b) converts concatemers to circular mtDNA molecules (c). 5′→3′ exonuclease produces a 3′ single-stranded tail of linear double-stranded mtDNA, followed end resection at DSBs (c–d). Homologous DNA recombinases such as Mhr1 initiate rolling-circle mtDNA replication in a heteroduplex joint (e), yielding replication intermediates (e–g) and products termed as concatemers, which are linear tandem multimers linked by head-to-tail unit-sized mtDNA (a). Intramolecular recombination (b) converts concatemers to circular mtDNA molecules (a), which may act as a template for rolling-circle mtDNA replication. Note: only circular mtDNA molecules (c) are resistant to degradation by exonuclease activities.