Figure 3.
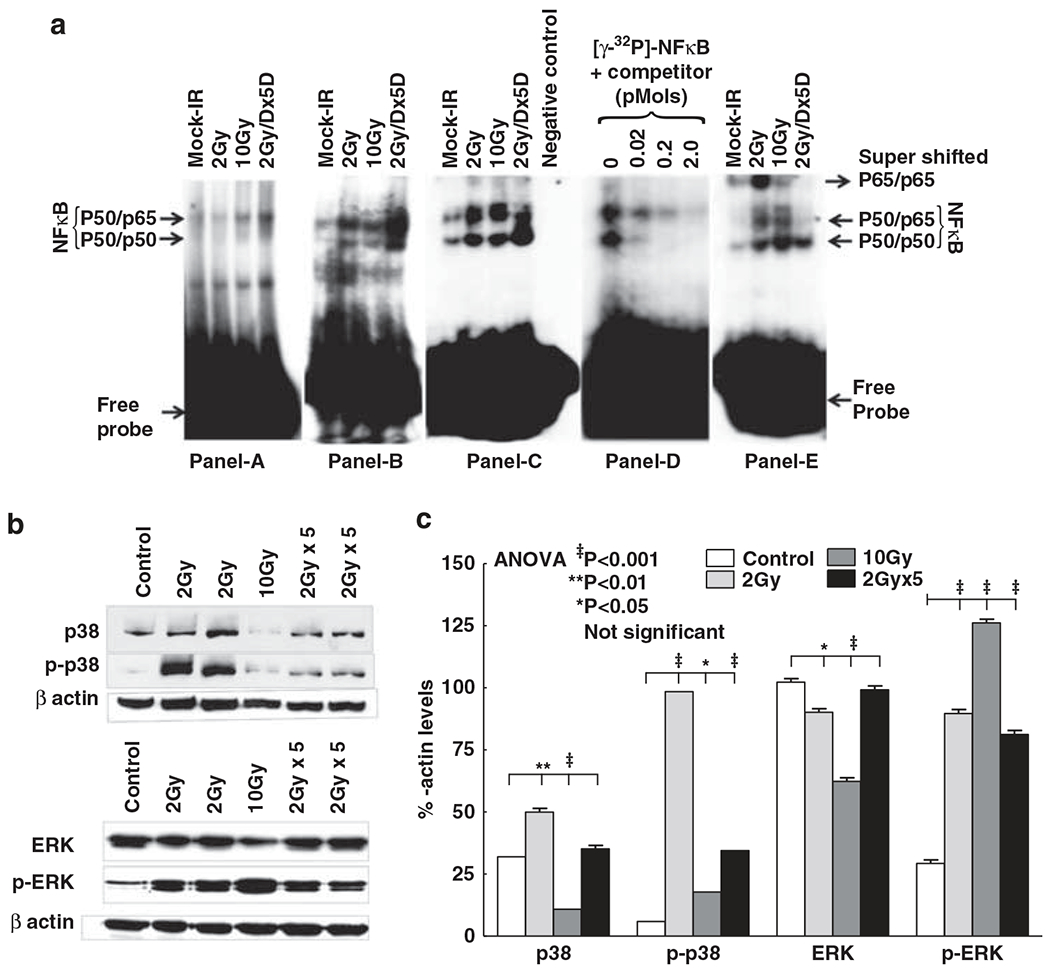
(a) Representative electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) autoradiograms (A–C) showing nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) DNA-binding activity in nontargeted heart tissues of mice exposed to 2 Gy, 10 Gy or fractionated ionizing radiation (FIR; 2 Gy per day for 5 days (2 Gy × 5D)). Specificity of NF-κB DNA-binding activity D). Nuclear protein was incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2, 3 and 4) of increased concentrations of homologous unlabeled competitor and probed with [γ-32P]-ATP-labeled NF-κB-specific oligonucleotide. Identification of NF-κB subunits by supershift assay (E). The addition of antibodies directed against potential components of NF-κB complex resulted in supershift when antibody of p65 was used. (b) Immunoblots showing total and phosphorylated p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 (ERK1/2) expression in nontargeted heart tissues of mice exposed to 2 Gy, 10 Gy or FIR (2 Gy × 5). (c) Histograms showing densitometry analysis of total and phosphorylated p38 and ERK1/2. The experiments were repeated at least three times and the group-wise comparisons were made using analysis of variance (ANOVA).
