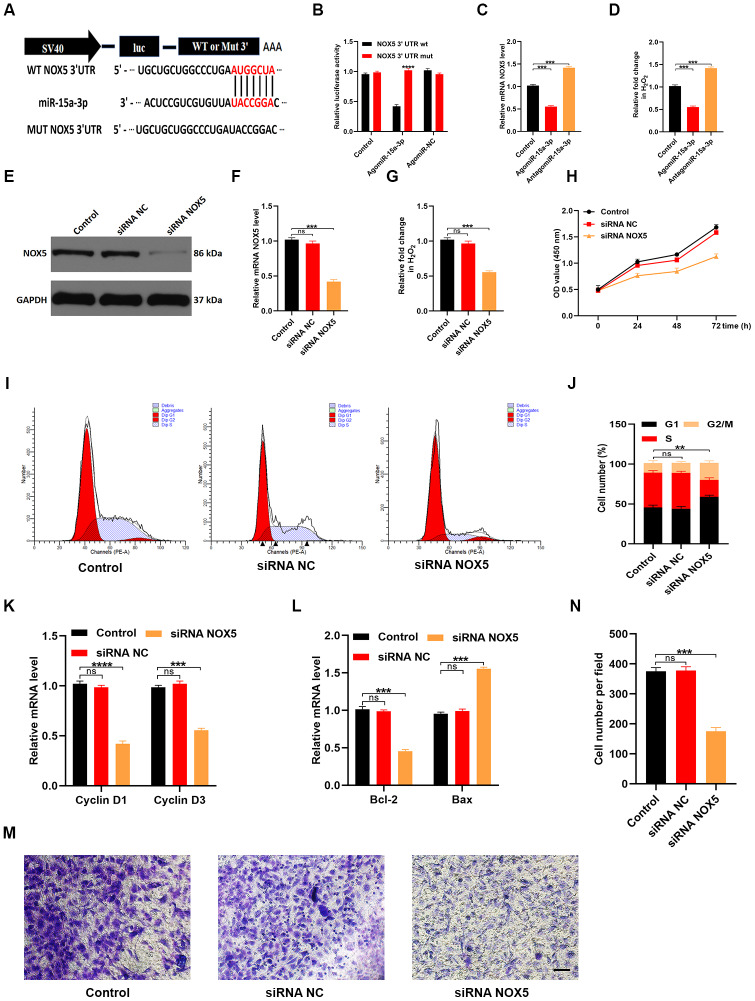
Figure 7.
MiR-15a-3p inhibits the NOX5/ROS signaling pathway. (A, B) The binding between miR-15a-3p and NOX5 was demonstrated with a luciferase reporter assay. (C) The effects of miR-15a-3p on NOX5 levels were assessed using qRT-PCR. (D) The intracellular release of ROS was measured in the three groups. (E, F) WB and qRT-PCR analyses were used to detect the efficacy of NOX5 siRNA. (G) The release of ROS decreased when NOX5 was silenced. (H) A CCK-8 assay was applied to assess cell proliferation after different treatments. (I, J) Flow cytometry was used to quantify the cell cycle distribution in treated cells. (K) The proliferation-related genes Cyclin D1 and Cyclin D3 were assessed using qRT-PCR. (L) The apoptosis-related genes Bcl-2 and Bax were assessed using qRT-PCR. (M, N) A Transwell migration assay was used to assess the effects of miR-15a-3p on HUVEC migration; scale bar: 100 μm. Data are the means ± SDs of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.