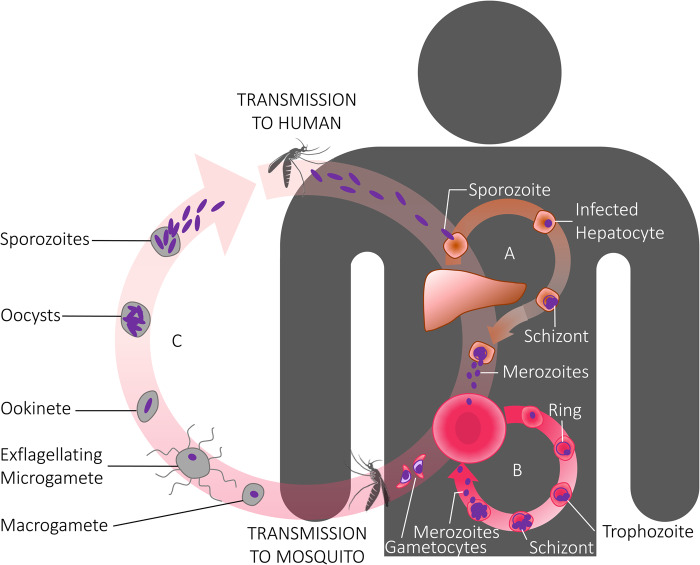
Figure 1. Stylized cartoon of the life cycle of the malaria parasite.
The life cycle commences in the vertebrate host with the bite of an infectious mosquito injecting sporozoite stages, and ends in the vertebrate host with the mosquito taking up sexual stages (gametocytes) to continue the life cycle in the definitive host — a female Anopheline mosquito. Gametocytes, within red blood cells, exist in the vertebrate host, whereas in the mosquito they emerge from the red cells to form female and male gametes, with the latter exflagellating to form microgametes which fertilize the female macrogametes.