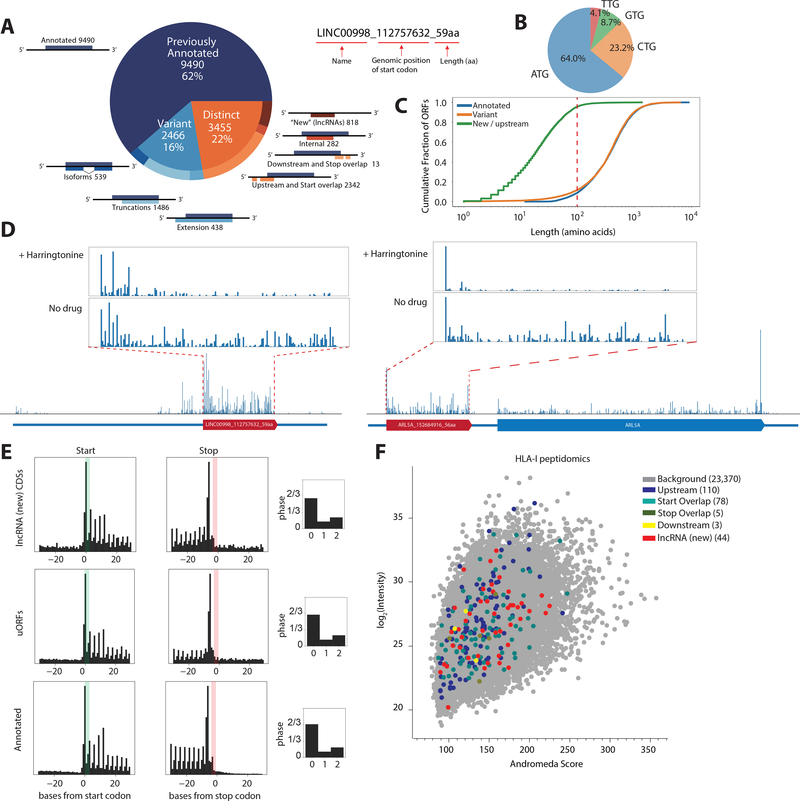
Fig. 1. Ribosome profiling reveals translation of unannotated CDSs.
(A) ORF-RATER analysis of ribosome profiling data: 62% are previously annotated coding sequences, while 16% are variants of canonical coding sequences that share portions of the coding sequence, and 22% are distinct from annotated coding sequences. The naming convention of the identified ORFs is shown on the right. (B) Start-codon usage of the identified CDSs. (C) Cumulative distribution of CDS length. For distinct CDSs, 96% are smaller than 100 amino acids. (D) Example ribosome profiling traces of a lncRNA peptide from LINC00998 and a uORF peptide from ARL5A displaying the hallmarks of translation, including peaks of density around the start codon following harringtonine treatment and three nucleotide periodicities along the coding region. (E) Metagene analysis shows that the signatures of translation, including three-nucleotide periodicity in the expected reading frame, for uORFs and lncRNA CDSs are similar to annotated coding regions. (F) Identification of more than 200 non-canonical CDS peptides from HLA-I peptidomics, cross-validating their existence across the whole abundance range, with a mean Andromeda score of 141 compared to a total mean Andromeda score of 144. See Methods.