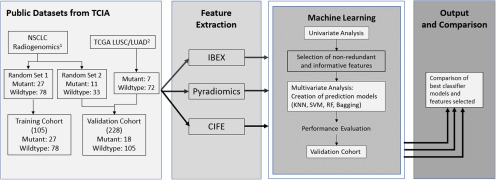
Figure 1.
Study design diagram. The design consists of 4 modules. First, projects NSCLC Radiogenomics and The Cancer Genome Atlas-Lung Adenocarcinoma (TGCA-LUSC)/TGCA-Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma (TCGA/LUAD) were obtained from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) and split into a homogenous training cohort and a heterogeneous validation cohort. Second, features were extracted from all imaging cases using 3 different feature extractors: IBEX, Pyradiomics, and CIFE. Third, univariate and multivariate analyses are sequentially conducted on features from each extractor to create prediction models for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation status. “x3” means the univariate and multivariate analyses were performed identically 3 times by using the features from IBEX, Pyradiomics, and CIFE. Finally, the best classifier models and optimal features are compared between the 3 individual extractors.
1NSCLC Radiogenomics was produced by Bakr et al. with 211 patients with NSCLC from Stanford University School of Medicine and the Palo Alto Veteran Affairs Healthcare System.
2TCGA-LUSC and -LUAD are projects of TCGA, consisting of lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma cases. Imaging is available from 5 centers in the United States (Washington University, University of Pittsburgh, UNC, Roswell Park, and Lahey Health Home).