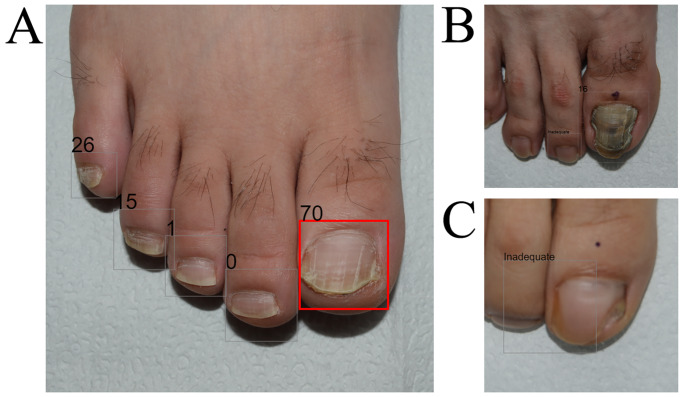
Fig 3. Examples of diagnostic output images.
(A) Correct example; a 24-year-old male, confirmed as having onychomycosis by KOH examination and culture. AI made an accurate diagnosis of onychomycosis using this image, whereas two of the five dermatologists misdiagnosed the case as onychodystrophy in the reader test. The rectangle was colored when the onychomycosis output was higher than the operating cut-off threshold (29.3; range 0–100). (B) Incorrect example; a 26-year-old male, confirmed as having onychomycosis by the KOH examination. AI made an inaccurate diagnosis of onychodystrophy using this image, whereas all five dermatologists correctly diagnosed the condition as onychomycosis. (C) Inadequate quality image; a 49-year-old female, confirmed as having onychomycosis by both KOH examination and culture study. AI first recognized the nail plate, and then the onychomycosis classifier determined whether the nail plate image was onychomycosis or not. With the low-quality, unfocused nail image, AI could not recognize the features properly, resulting in an unreliable diagnostic prediction.