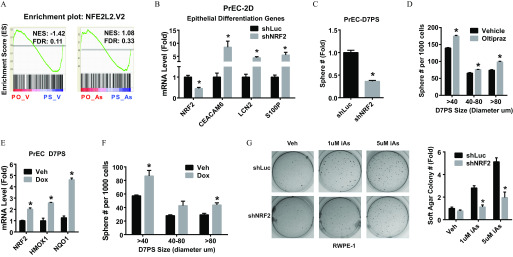
Figure 3.
The role of NRF2 plays in iAs-induced transformation. (A) GSEA data of NRF2 pathway genes comparing prostate organoids (PO) and spheres (PS) derived from primary human prostate epithelial cells (PrEC) and treated with vehicle (PO-V vs. PS-V) or arsenic (PO-As vs. PS-As). (B) Expression of prostate epithelial differentiation genes in 2-dimensional culture PrEC (PrEC-2D) with NRF2 knockdown (shNRF2). Data shown are (); * vs. shRNA control (shLuc). (C) Sphere formation capability of PrEC with NRF2-knockdown, D7PS: day-7 spheres. Data shown are (); * vs. vehicle. (D) Quantification of sphere formation capability of PrEC treated with NRF2-inducer Oltipraz () for 7 d. D7PS: day-7 prostate spheres. Data shown are (); * vs. vehicle. (E) mRNA level of NRF2 gene and NRF2 pathway marker genes. Tet-On NRF2 expression was induced in PrEC spheres by lentivirus. Spheres were (Dox, ) for 7 d (Tet-ON-NRF2 PrEC-D7PS) to induce NRF2 overexpression. Data shown are (); * vs. vehicle. (F) Quantification of sphere formation capability of PrEC with Tet-On overexpression of NRF2. Data shown are (); * vs. vehicle. (G) Soft-agar colony formation assay of RWPE1 with indicated treatment. Note: iAs, inorganic arsenic; shLuc, RWPE1 with shRNA targeting luciferase gene, negative control; shNRF2, RWPE1 with NRF2 knockdown. Data shown are (); * vs. shRNA control (shLuc).