Fig. 4. 3D super-resolution reconstruction of immunofluorescence-labeled Nup98 on the nuclear envelope in COS-7 cells.
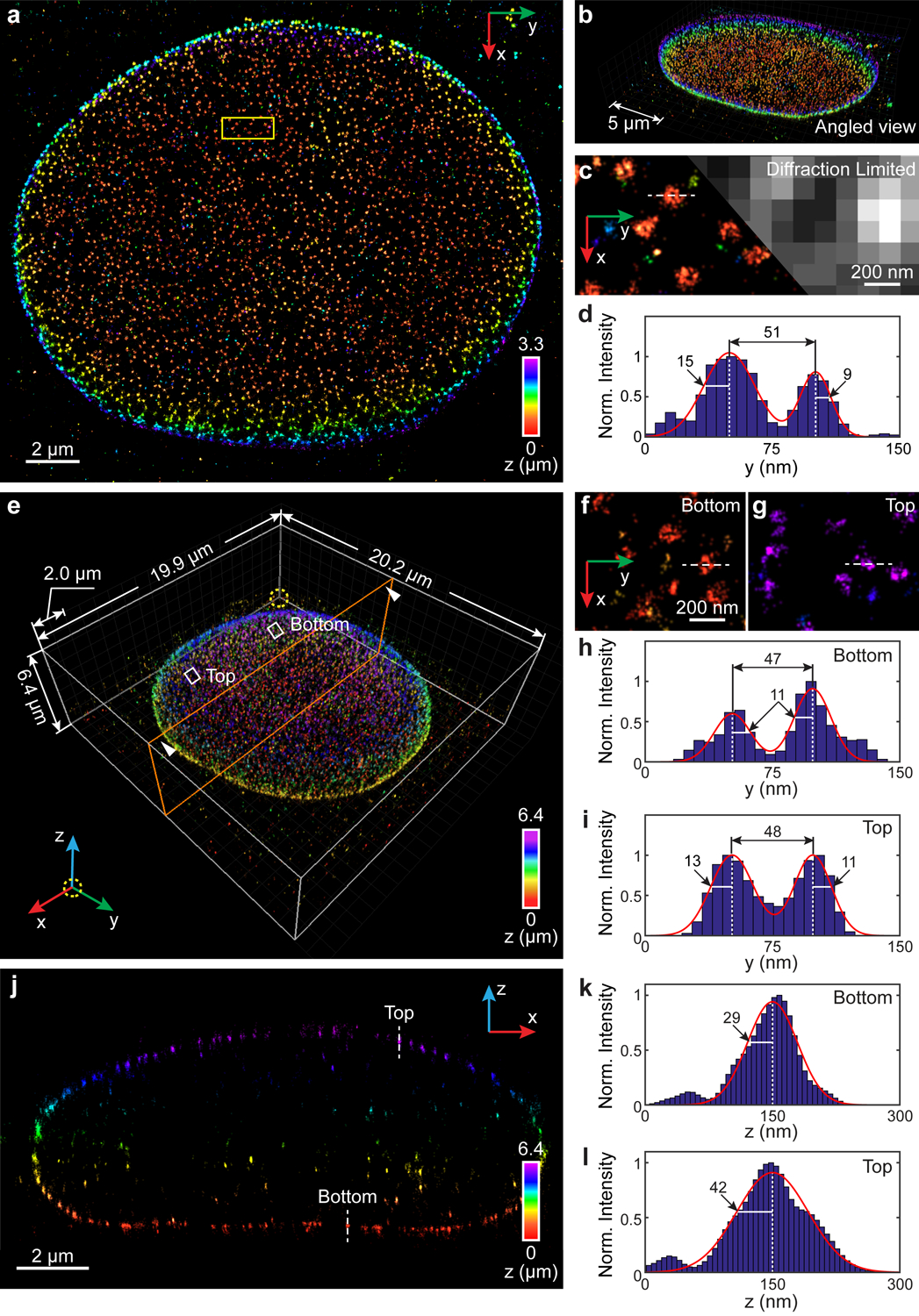
(a) x-y overview of a 3.3-μm-thick volume of the nucleus. (b) Angled view of (a). (c) Sub-region as indicated by the yellow boxed region in (a) showing the ultra-structure of Nup98 (left), which is not resolvable in conventional diffraction-limited microscopy (right). (d) Intensity profile along the white dashed line in (c). The diameter of this Nup98 structure is 51 nm, while σy obtained from the left and right boundaries equals to 15 nm and 9 nm, respectively. (e) Nup98 on the 6.4-μm-thick entire nuclear envelope rendered in 3D. An animated 3D reconstruction is shown in Supplementary Video 5. (f,g) Sub-regions as indicated by the white boxed regions in (e) showing enlarged x-y views of resolved nuclear pores at both bottom (f) and top (g) surfaces. (h,i) Intensity profiles along the white dashed lines in (f,g). The diameters of the Nup98 structures are 47 nm and 48 nm at the bottom (h) and top (i) surface, respectively. The numbers near the black arrows indicate σy in nanometers, which has a mean value of 11.5 nm. (j) x-z cross section along the orange plane in (e). The integration width of the x-z cross section in the y direction is 500 nm. (k,l) Intensity profiles along the white dashed lines in (j). σz equals to 29 nm and 42 nm for the measured structure at the bottom (k) and top (l) surface, respectively. The datasets shown are representative of four datasets of ~3 μm-thick volumes of nucleus and six datasets of the entire nuclear envelope. Norm.: normalized.
