Extended Data Fig. 2. Performance quantification of INSPR in biplane setup.
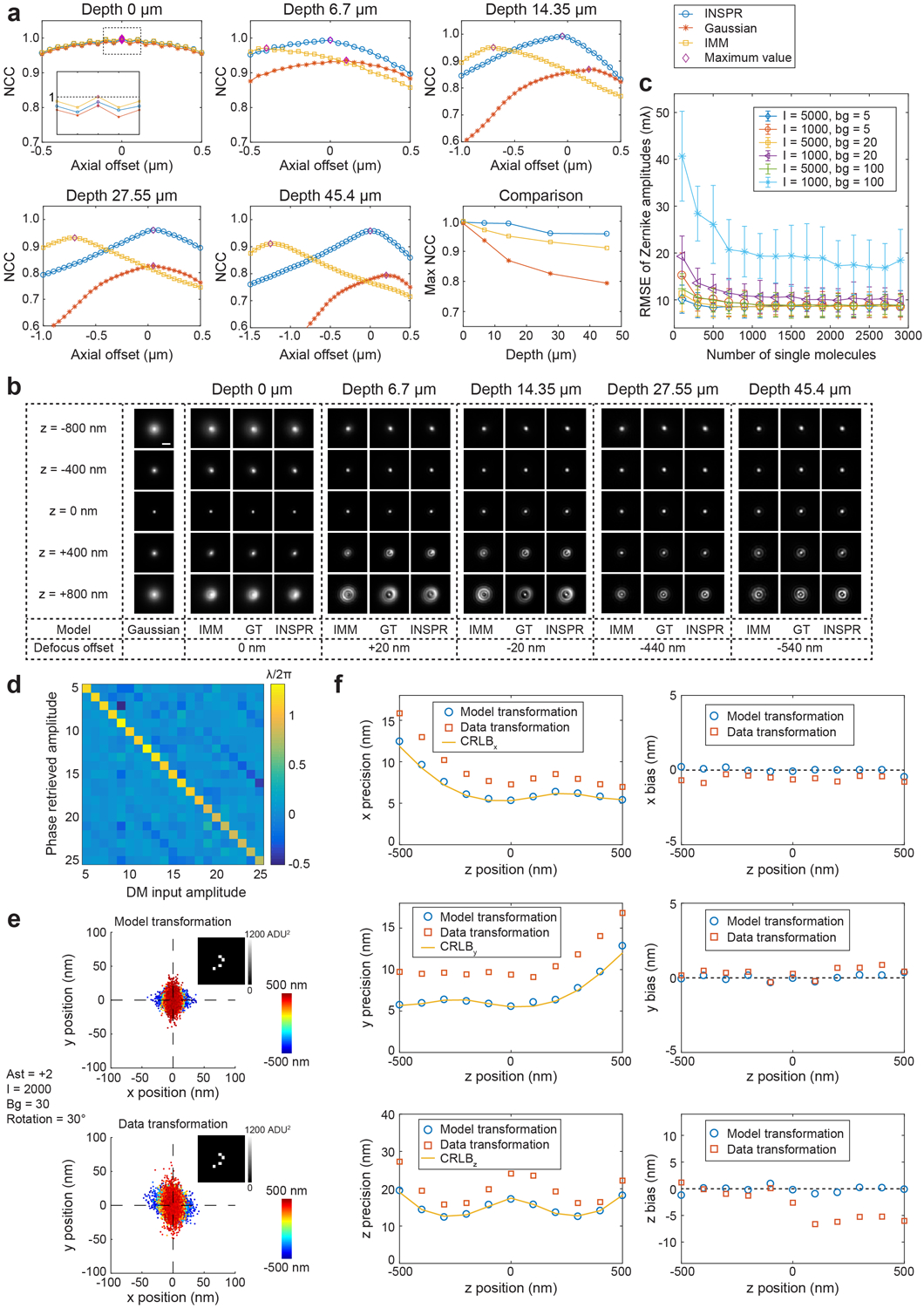
(a) Similarity between the ground truth 3D PSFs and the 3D PSFs at different imaging depths when using INSPR (blue circles), Gaussian model (orange stars), and theoretical index mismatch model (IMM, yellow squares). For each depth, 3D normalized cross correlation (NCC) coefficients between the ground truth PSFs and the PSFs generated using three methods at different axial offsets are shown, with the maximum values marked (purple diamonds). (b) 3D PSFs retrieved using Gaussian, IMM, and INSPR in comparison to the ground truth (GT) at different depths, when NCC reaches the maximum at each depth (purple diamonds in (a)). The defocus offset (i.e., the axial shift from the actual focal plane) is obtained by finding the maximum-intensity plane of the ground truth PSFs along the axial direction. Scale bar: 1 μm. (c) Root-mean-square error (RMSE) between the decomposed Zernike amplitudes of INSPR retrieved model and the ground truth amplitudes in different photon (I) and background (bg) conditions. In each condition, the amplitudes of the ground truth are randomly sampled from −1 to +1 (unit: λ/2π) for each trial (11 trials in total). (d) Heat map showing the relationship between the input and phase retrieved amplitudes of 21 Zernike modes. (e) Scatter plots of lateral localizations using model transformation (top) and data transformation (bottom) for PSFs with vertical astigmatism (Ast). The total photon count per emission event I is 2000, and the background count per pixel bg is 30. Plane 1 and plane 2 are related with an affine transformation including a rotation of 30 degrees. Both Poisson noise and pixel-dependent sCMOS readout noise (the variance distribution is shown in the inset) are considered. (f) Localization precisions and biases in the x, y, and z dimensions for the dataset in (e).
