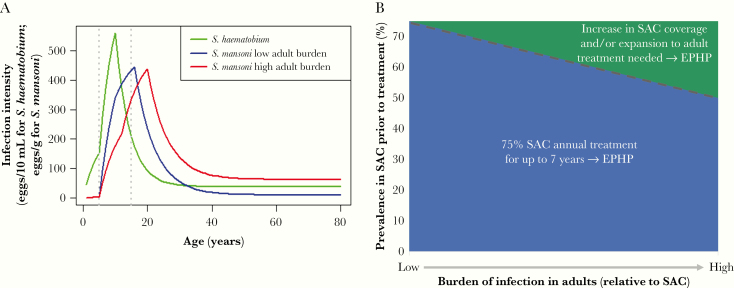
Figure 1.
A, Age-intensity profiles of infection for Schistosoma mansoni using model-simulated low and high adult burdens of infection (relative to school-aged children [SAC; 5–14 years old]) and S. haematobium using previous fit to data [15]. B, Schematic showing treatment strategies required for achieving elimination as a public health problem (EPHP). Low adult burden of infection settings based on modeling insights on S. mansoni with a low adult burden setting and on S. haematobium. High adult burden of infection settings based on modeling insights on S. mansoni with a high adult burden setting. Blue region, 75% SAC-only annual treatment for up to 7 years is sufficient for achieving EPHP; green region, increase in school-based treatment coverage (ie, over 75% SAC annual treatment for 7 years) and/or expansion to community-wide treatment is needed for achieving EPHP (dashed line, approximate prevalence threshold above which this occurs for given age profiles).