Figure 6. Effects of kinase inhibitors on SNACS fluorescence emission ratios in guard cells.
SNACS responses in guard cells were analyzed in the pUBQ10:OST1-HF-expressed in the ost1-3 genetic background. The ratio of YPet to Turquoise GL emission was normalized to the average value over the 5 min before K252a application. (A) The protein kinase inhibitor K-252a reduced SNACS FRET ratio in vivo, and ABA did not induce a ratio increase in the presence of K-252a. After 10 min incubation with 10 µM K-252a, 20 µM ABA was added. (B) ABA induced a ratio increase in the presence of DMSO (0.2%, solvent control for K-252a). (C) The kinase inhibitor K-252a inhibited SnRK2 kinase activity after ABA treatment. (D) Control experiment for C. 0.2% DMSO was added. (E) Kinase inhibitor W7 did not affect SNACS FRET ratio in vivo. After 10 min incubation with 20 µM W7, 20 µM ABA was added. (F) Control experiment for E. 0.1% DMSO was added as solvent for W7.
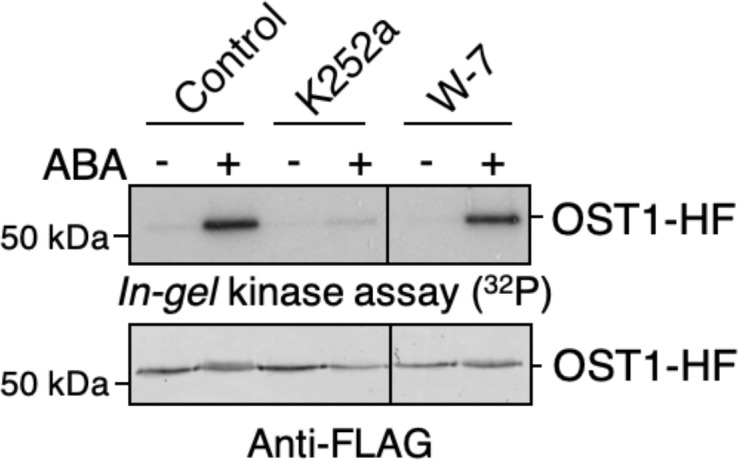
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. W-7 does not have a clear effect on ABA-induced OST1/SnRK2.6 activation in plant cells.