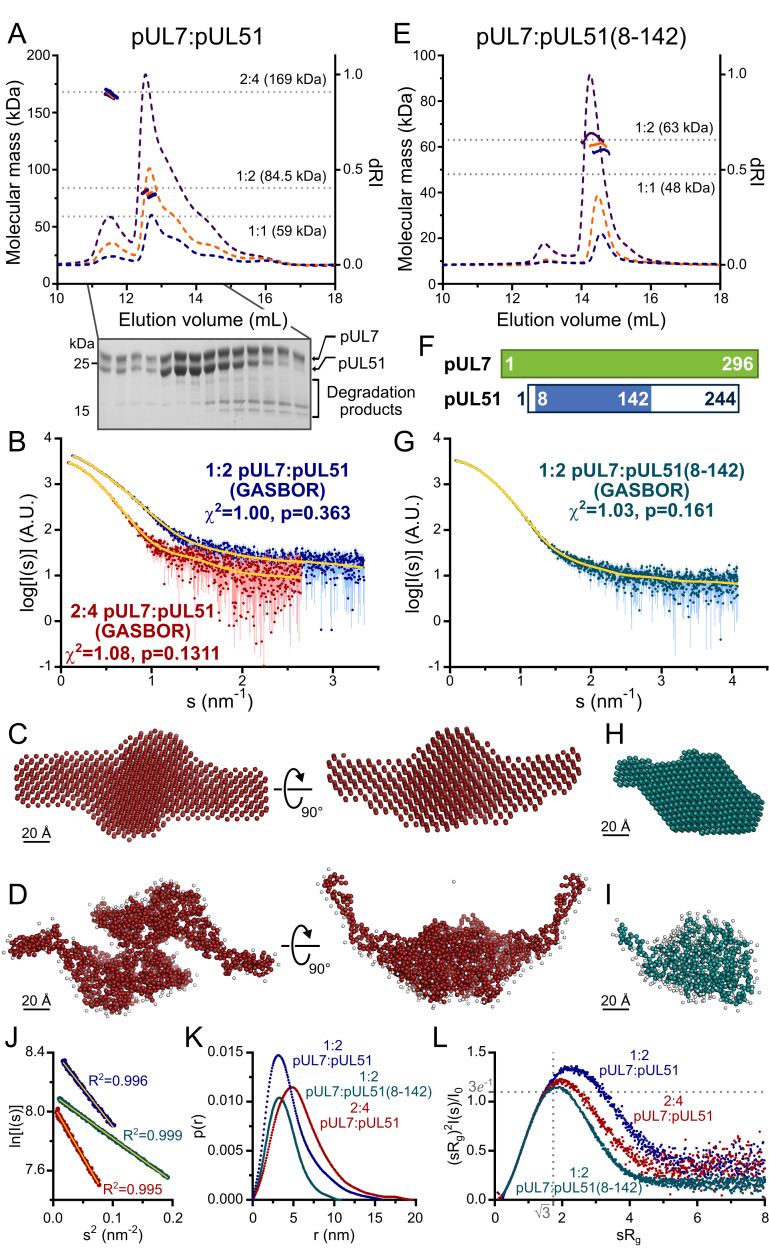
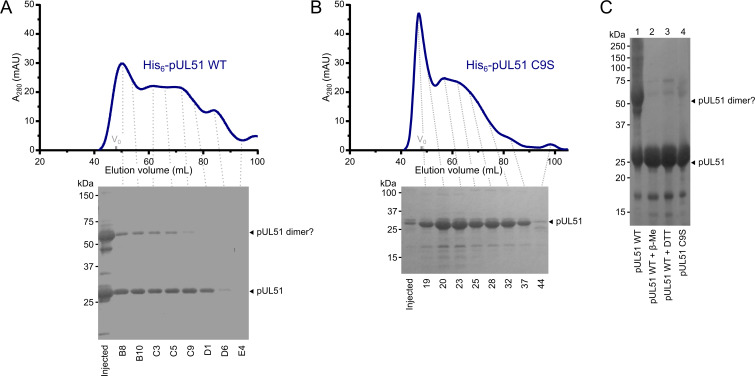
Figure 1. HSV-1 pUL7:pUL51 forms a 1:2 heterotrimeric complex in solution.
(A) SEC-MALS analysis of recombinant full-length pUL7:pUL51 complex. Weight-averaged molecular masses (colored solid lines) are shown across the elution profiles (normalized differential refractive index, dRI, colored dashed lines) for samples injected at 2.4, 4.9 and 9.7 mg/mL (blue, orange and purple, respectively). The expected molecular masses for 1:1, 1:2 and 2:4 pUL7:pUL51 complexes are shown as dotted horizontal lines. (B) Averaged SAXS profiles through SEC elution peaks corresponding to 1:2 (blue) and 2:4 (red) complexes of pUL7:pUL51. Fits of representative GASBOR ab initio dummy-residue models to the scattering curves for each complex are shown in yellow. χ2, fit quality. p, Correlation Map (CorMap) P-value of systematic deviations between the model fit and scattering data (61). (C) Refined DAMMIN dummy-atom model reconstruction of the 2:4 pUL7:pUL51 complex, shown in two orthogonal orientations. (D) Representative GASBOR dummy-residue model of the 2:4 pUL7:pUL51 complex, shown in two orthogonal orientations. This model comprises an anti-parallel dimer of heterotrimers, although we note that parallel dimers are also consistent with the scattering data. (E) SEC-MALS of pUL7:pUL51(8-142) complex. Elution profiles and molecular masses are shown as in (A) for recombinant pUL7:pUL51(8–142) injected at 0.6, 1.1 and 3.9 mg/mL (blue, orange and purple, respectively). (F) Schematic representation of pUL7 and pUL51. (G) Averaged SEC-SAXS profile through pUL7:pUL51(8–142) elution peak. Fit of a representative GASBOR ab initio dummy-residue model to the scattering curve is shown in yellow. (H) Refined DAMMIN dummy-atom model reconstruction of pUL7:pUL51(8–142) complex. (I) Representative GASBOR dummy-residue model of pUL7:pUL51(8-142). (J) Plot of the Guinier region (sRg < 1.3) for SAXS profiles shown in (B) and (G). The fit to the Guinier equation (yellow) is linear for each curve, as expected for aggregate-free systems. (K) p(r) vs r profiles for SAXS profiles shown in (B) and (G). (L) Dimensionless Kratky plot of SAXS profiles shown in (B) and (G). The expected maximum of the plot for a compact globular domain that conforms to the Guinier approximation is shown (sRg = √3, (sRg)2I(s)/I0 = 3e−1, grey dotted lines).