Figure 2.
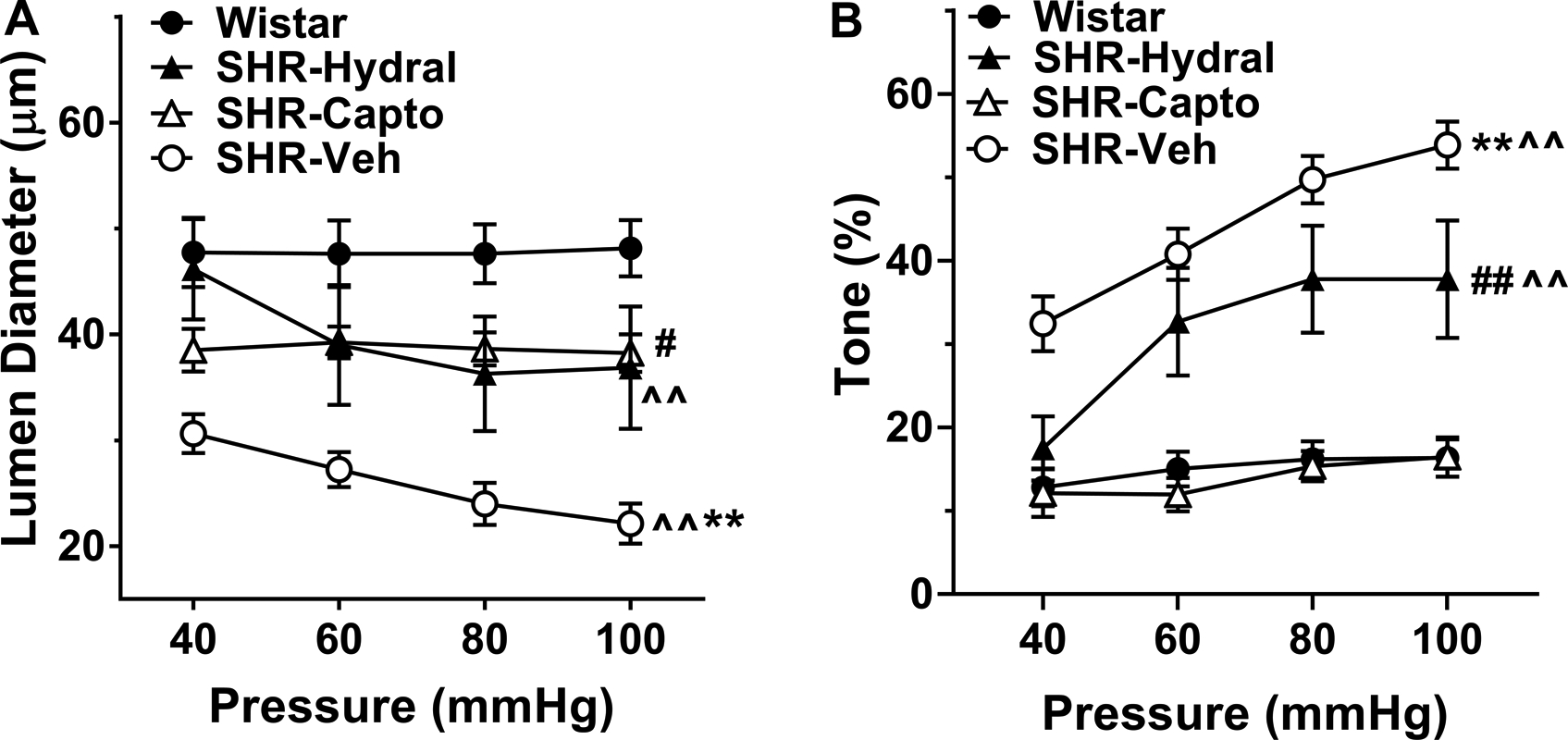
Myogenic reactivity and percent myogenic tone to increased intravascular pressure in LMAs isolated from Wistar rats, and SHRs with or without treatment. A, Change in active lumen diameter in response to increased intravascular pressure of LMAs from Wistar rats, SHRs treated with hydralazine, captopril or vehicle. There was a significant group by pressure interaction, a group effect and pressure effect [F(9, 81)=5.71, F(3, 27)=9.07, F(3, 81)=15.46; P<0.01)]. ^^P<0.01, indicating significant pressure effect in SHR-Veh and SHR-Hydral groups; **P<0.01 vs. all groups, #P<0.05 vs. Wistar rats by mixed model repeated measures ANOVA. B, Percent myogenic tone at different intravascular pressures of LMAs from Wistar rats, SHRs treated with hydralazine, captopril or vehicle. There was a significant group by pressure interaction, as well as a group effect and pressure effect [F(9, 81)=4.75, F(3, 27)=23.71, F(3, 81)=27.17; P<0.01]. ^^P<0.01, indicating significant pressure effect in SHR-Veh and SHR-Hydral groups; **P<0.01 vs. all groups, ## P<0.01 vs. Wistar and SHR-Capto by mixed model repeated measures ANOVA. Wistar: n=8; SHR-Hydral: n=7; SHR-Capto: n=8; SHR-Veh: n=8.
