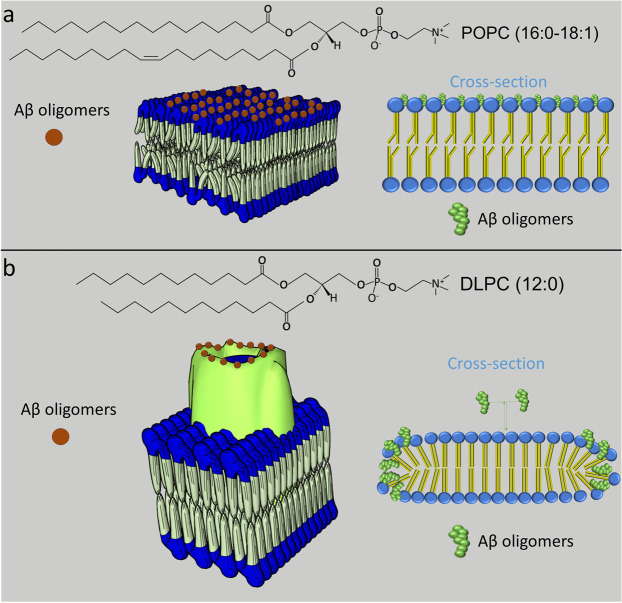
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanism of Aβ monomer/oligomer attachment to two different lipid membranes, POPC (a) and DLPC (b). In this model, Aβ insertion into the membrane is energetically more favourable for DLPC as it relieves the mechanical strain caused by the highly curved regions of the membrane patches, which in turn promotes Aβ aggregation by enhancing its local concentration. The shape of the Aβ assemblies resembles that of the membrane patches. Aβ oligomers coloured in brown interact with defects on the edges of multiple bilayers of DLPC which create hotspots for Aβ attachment.