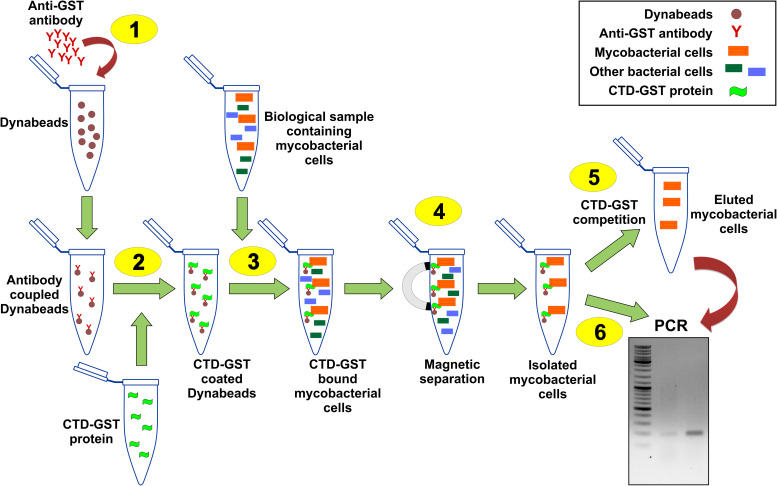
FIGURE 3.
Schematic of CTD-based mycobacterial detection assay. Illustration here shows the general procedure for the isolation of M. smegmatis cells present in a given biological sample. 1–6 represent the key steps in the assay as detailed in “Methods” section. Step 1 is the coupling of anti-GST antibodies with Dynabeads. CTD-GST protein is then coated on these beads (Step 2). Step 3 involves the incubation of mixed bacterial sample having M. smegmatis cells with the product of step 2. Step 4 involves magnetic separation of the Dynabeads that pulls down M. smegmatis cells. The isolated cells can either be eluted by competition with CTD-GST (Step 5) or be used directly in a PCR (Step 6).