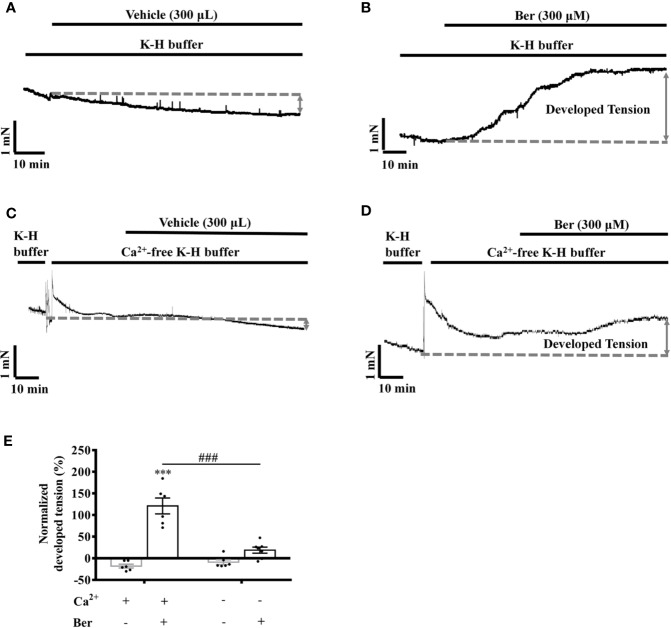
Figure 6.
The removal of extracellular Ca2+ hindered the berberine-induced tension increase in left ventricular muscle (LVM) strips. (A–D) Original isometric tension recordings of the LVM strips treated with vehicle (A), 300 μM Ber (B); vehicle (C) and 300 μM Ber (D) under the Ca2+-free condition, respectively. (E) Summary data showing that the removal of extracellular Ca2+ significantly reduced the ability of berberine to increase the tension of LVM strips. The numbers of repeats are as follows: vehicle control of 300 µM Ber, n = 6, N = 6; 300 µM Ber, n = 6, N = 6; vehicle control of 300 µM Ber in the Ca2+-free Krebs-Hensseleit (K-H) buffer, n = 6, N = 6; 300 µM Ber in the Ca2+-free K-H buffer, n = 7, N = 7; n and N are the numbers of LVM strips and rats, respectively. Ber stands for berberine. ***p < 0.001 vs. vehicle control group; ###p < 0.001 vs. Ber-treated group in the normal K-H buffer; two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test.