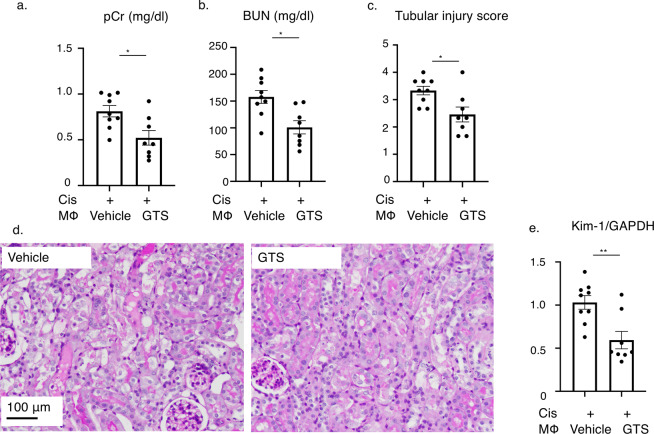
Figure 3.
Adoptive transfer of α7nAChR agonist GTS-21-treated macrophages improved renal outcome. (a–c) Plasma creatinine, BUN, and histology score are significantly reduced by GTS-treated macrophage transfer (plasma creatinine: 0.81 ± 0.06 and 0.51 ± 0.07 mg/dl, P = 0.0105; BUN: 157.8 ± 11.4 and 101.0 ± 11.6 mg/dl, P = 0.0051; histology score: 3.33 ± 0.15 and 2.46 ± 0.26, P = 0.0122; for Cis-vehicle-treated macrophage and Cis-GTS-treated macrophage, respectively; n = 8 or 9). (d) Representative pictures of PAS-staining. (e) The expression level of Kim-1 mRNA in the whole kidney was also decreased by GTS-21-treated macrophage transfer (relative expression of Kim-1: 1.031 ± 0.07 and 0.59 ± 0.09, P = 0.0034; for Cis-vehicle-treated macrophage and Cis-GTS-treated macrophage, respectively; n = 8 or 9). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Scale bar, 100 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (two-way analysis of variance followed by the Sidak post-hoc test). BUN, blood urea nitrogen; VNS, vagus nerve stimulation; Cis, cisplatin; SEM, standard error of the mean; GTS, GTS-21; PAS, periodic acid-Schiff.