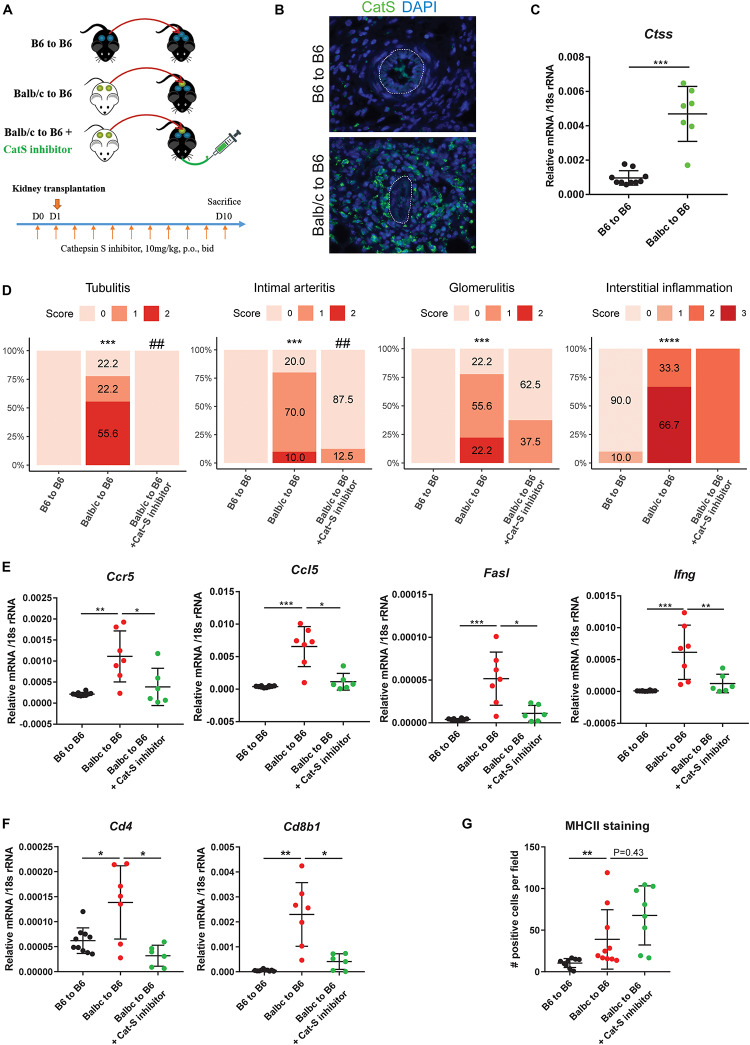
FIGURE 4.
Cathepsin S inhibition attenuated renal allograft rejection in vivo. (A) Experimental design. Wild-type C57BL/6 kidneys (syngeneic) or wild-type Balb/c kidneys (allogeneic) were transplanted into wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Allogenic recipients were orally administrated with either vehicle or Cat-S inhibitor 10 mg/kg twice daily for a total of 11 days. At day 10 after transplantation, mice were analyzed. (B) Cat-S staining in mouse kidney grafts from syngeneic (B6 to B6) and allogeneic group (Balb/c to B6). White dash lines represent for vessels. Magnification 200×. (C) Ctss mRNA expression in mouse kidney grafts. (D) Histological score for mouse kidney grafts. Tubulitis, intimal arteritis, glomerulitis, and interstitial inflammation were quantified by Banff scoring method. ***p < 0.001 Balb/c to B6 vs. B6 to B6; ****p < 0.0001 Balb/c to B6 vs. B6 to B6; ##p < 0.01 Balb/c to B6 vs. Balb/c to B6 + Cat-S inhibitor. N = 10 for B6 to B6, n = 9–10 for Balb/c to B6, n = 8–10 for Balb/c to B6 + Cat-S inhibitor. (E) Proinflammation gene expression in mouse kidney grafts by RT-qPCR. (F) Cd4 and Cd8b1 gene expression in mouse kidney grafts. (G) Quantification of interstitial MHC-II positive cells in mouse kidney graft. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. B6 represents for C56BL/6J.