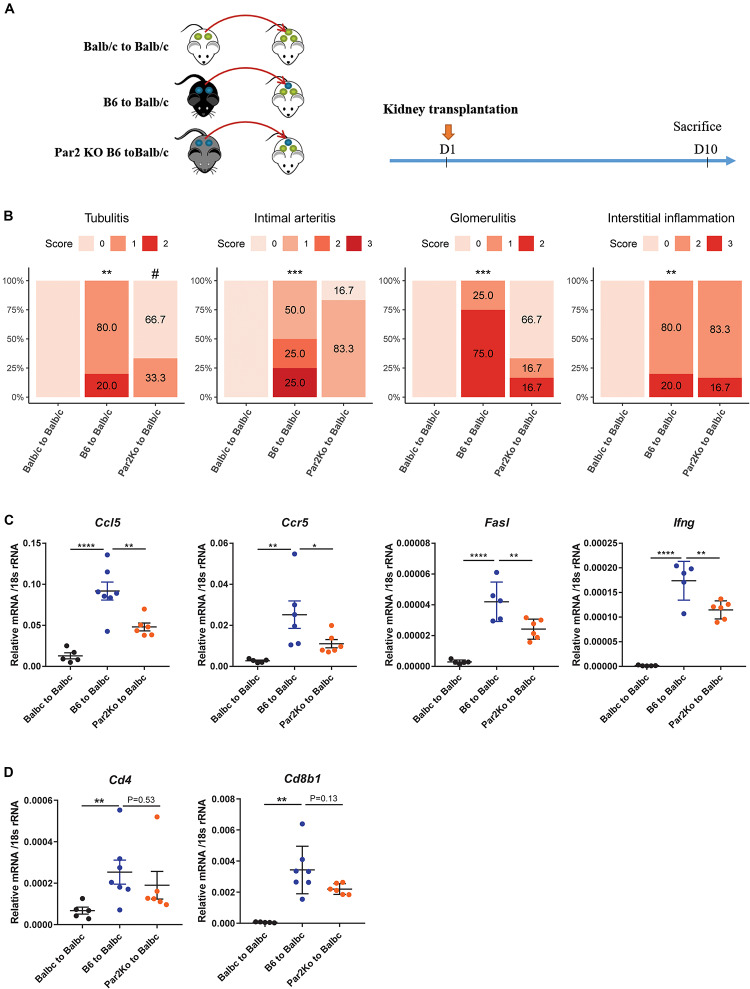
FIGURE 5.
Par2 deficiency in grafts attenuated renal allograft rejection in vivo. (A) Experimental design. Wild-type Balb/c kidneys (syngeneic) or wild-type C57BL/6 (allogeneic) were transplanted to wild-type Balb/c mice. Par2-deficient kidneys from C67BL/6 background (allogeneic) were transplanted into wild-type Balb/c mice. At day 10 after transplantation, mice were sacrificed for analysis. (B) Histological score for mouse kidney grafts. Tubulitis, intimal arteritis, glomerulitis, and interstitial inflammation were quantified by the Banff scoring method. **p < 0.01 B6 to Balb/c vs. Balb/c to Balb/c, ***p < 0.001 B6 to Balb/c vs. Balb/c to Balb/c, #p < 0.05 B6 to Balb/c vs. Par2KO to Balb/c. N = 4 for Balb/c to Balb/c, n = 4–6 for B6 to Balb/c, n = 6 for Par2KO to Balb/c. (C) Proinflammation gene expression in mouse kidney grafts by RT-qPCR. (D) Cd4 and Cd8b1 gene expression in mouse kidney grafts. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. B6 represents for C56BL/6J. Par2KO represent for Par2 deficiency.