Figure 1.
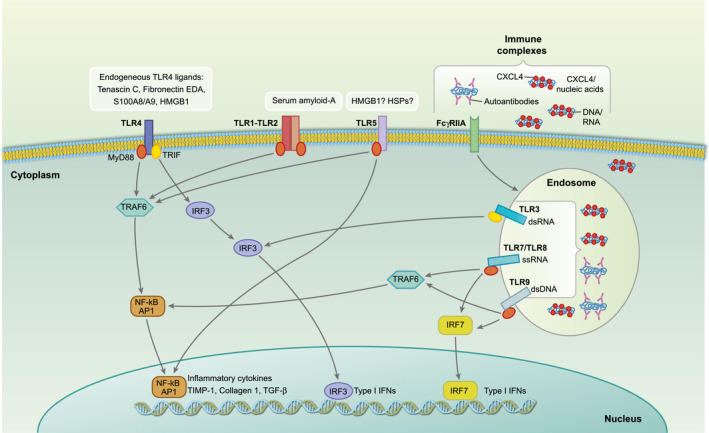
Endogenous Toll‐like receptor (TLR) ligands identified in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Binding of danger‐associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) (released by injured tissues) to TLR‐4 and TLR‐1 and ‐2 triggers the production of inflammatory cytokines [interleukin (IL)‐6, IL‐8, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)‐α, transforming growth factor (TGF)‐β], as well as factors involved in the extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, such as the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP‐1) and collagen 1. Whether TLR‐5 is triggered by endogenous ligand in SSc is unknown (possible candidates may be high‐mobility group protein 1 (HMGB1) or heat shock proteins (HSPs), according to studies in other settings (see text). SSc–immune complexes (SSc–IC), which include autoantibodies anti‐topoisomerase antibodies (ATA) and anti‐centromere antibodies (ACA), etc. as well as nanocristalline particles of platelet‐ and platelet dendritic cell (pDC)‐derived chemokine C‐X‐C ligand motif (CXCL4) bound to nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) can stimulate endosomal nucleic‐acid sensing TLRs TLR‐7, TLR‐8, TLR‐9 and TLR‐3, once internalized. SSc–IC also induces IL‐6, IL‐8, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)‐2, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP‐1), TGF‐β1 and pro‐collagen α1 by fibroblasts.
