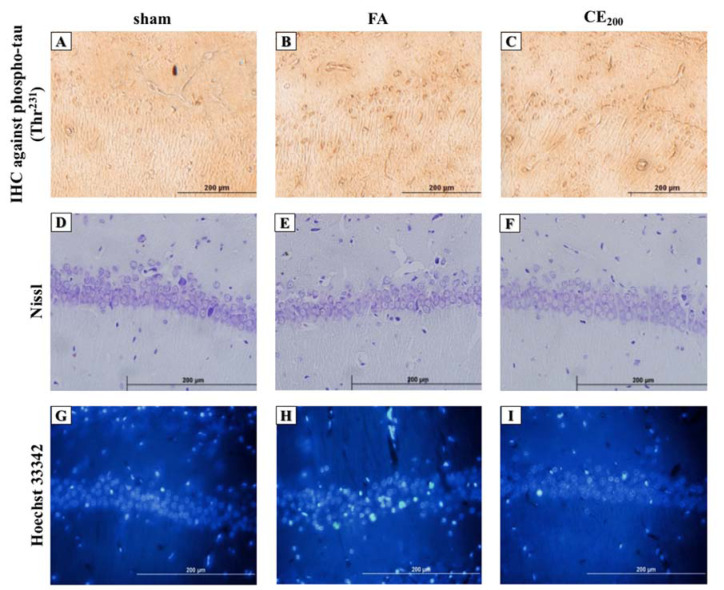
Figure 4. Histological alterations of the CA1 area of the hippocampus following treatments (200x). Formaldehyde administration caused a prominent increase in the amounts of phospho-tau in the cytoplasm of the pyramidal cells in the CA1 area of the hippocampus (B) compared to control (A). Cells representing nuclear damage are shown to be increased in the FA group (H) compared to control (G). When treated with CE at the dose of 200 mg/kg the amounts of phospho-tau (C) and cells with nuclear damage (I) notably decreased. There were no differences in cell morphology between groups (D, E, F).
sham: no treatment, FA: formaldehyde 60 mg/kg, CE200: FA 60 mg/kg + methanolic cinnamon extract 200 mg/kg.