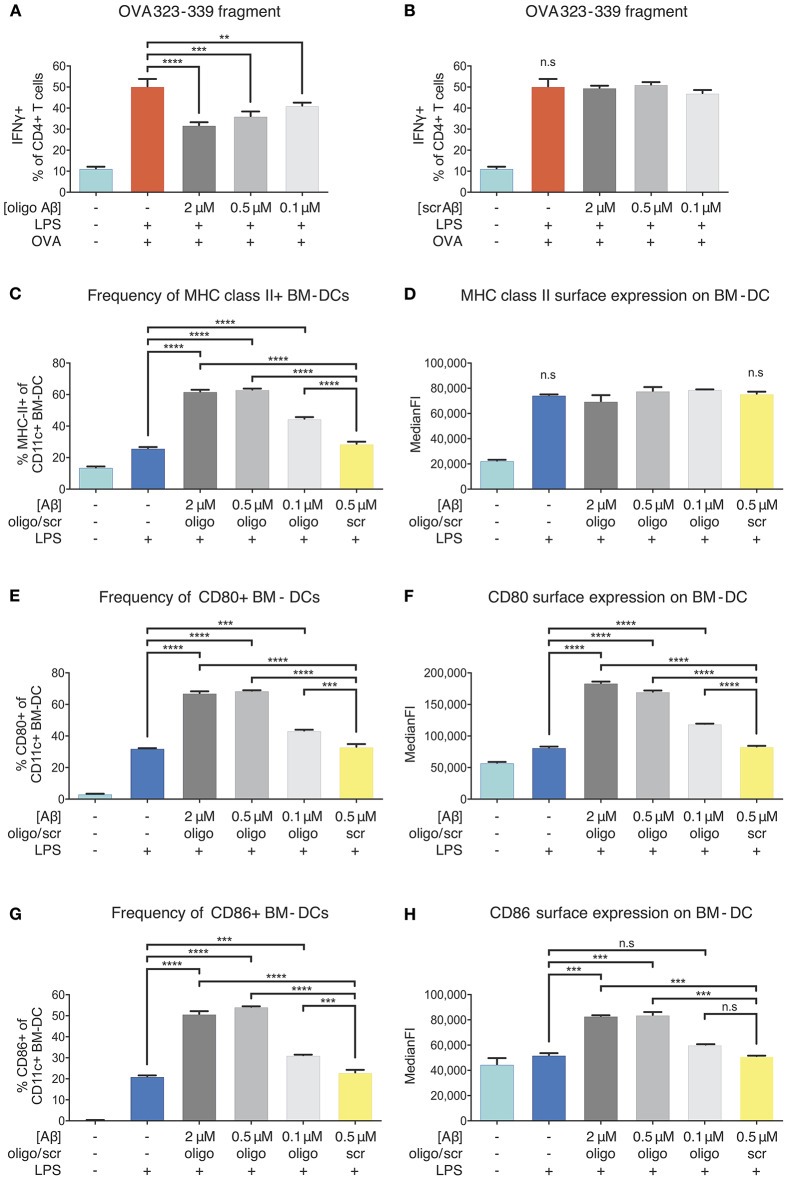
Figure 5.
Inhibition of APCs by Aβ1-42 oligomers in vitro without involvement of antigen-processing and -presenting apparatus. The effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on antigen-processing was tested by using OVA 323-339, a fragment that leads to robust OT-II T-cell response without intracellular processing. Addition of Aβ1-42 oligomers (A), but not scrambled (scr) peptide (B), inhibits T-cell activation in a dose-dependent manner, indicating that inhibitory effects of Aβ1-42 oligomers are independent of APCs' antigen-processing machinery. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of surface MHC-II expression shows that Aβ1-42 oligomers (but not scr peptide) increase MHC-II+ BM-DC frequencies. (D) In comparison with LPS-matured BM-DCs, no changes in surface MHC-II expression per cell (median fluorescent intensity = MedianFI) is detectable after applying Aβ1-42 oligomers to in vitro antigen presentation assays. (E,G) Analysis of surface co-stimulatory factor CD80/CD86 expression shows that Aβ1-42 oligomers (but not scr peptide) increase CD80+/CD86+ BM-DC frequencies. (F,H) In comparison with LPS-matured BM-DCs, surface expression of CD80/CD86 per cell (measured by MedianFI) is further increased after applying Aβ1-42 oligomers. Representative results of at least 3 independent experiments are shown in each graph; n ≥ 2 per treatment condition in each experiment. (Data are shown as mean ± SD, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, n.s. = non-significant, one-way ANOVA).