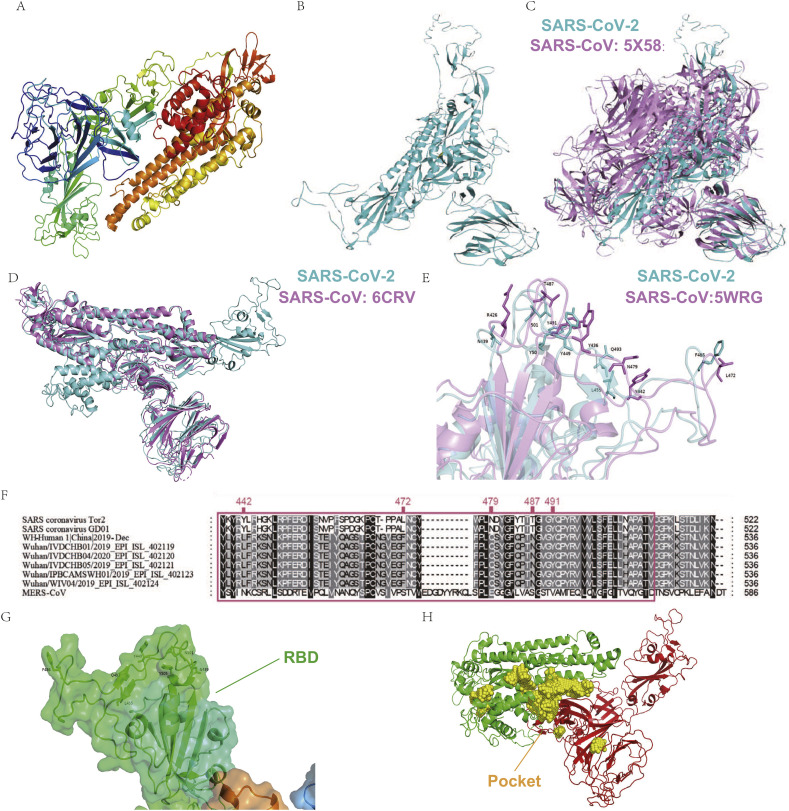
Fig. 1.
The tertiary structure of SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) protein and the pocket for drug screening.
The tertiary structure of SARS-CoV-2 S protein was acquired via homology modeling (A) or ab initio model (B, cyan). (C) Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 S protein (cyan) and SARS-CoV S protein 5 × 58 (mauve). (D) Identification of SARS-CoV-2 S protein RBD (cyan) by comparing to SARS-CoV S protein 6CRV (mauve). (E) Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 S protein RBD (cyan) with SARS-CoV 5WRG RBD (mauve). (F) Comparison of RBD amino acid sequences between different strains of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. (G) The RBD of S protein (green area) show insufficient stability for future drug screening. (H) The selected binding pocket (yellow area) for drug screening,