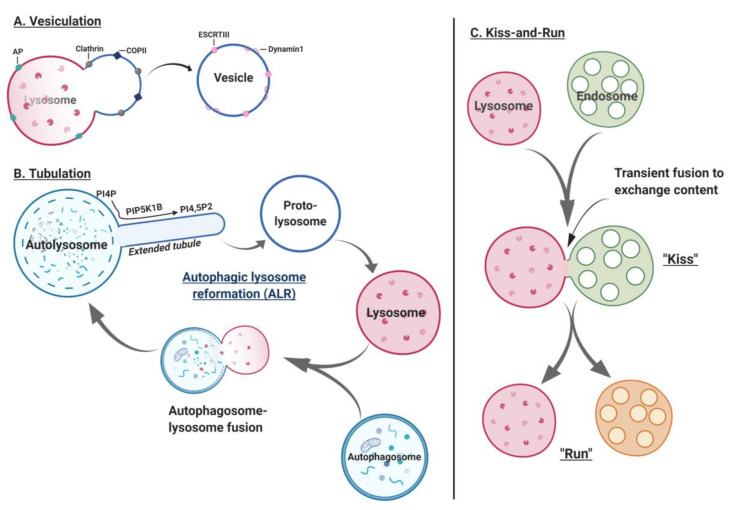
Figure 5.
Lysosome fission. Lysosome fission involves, vesiculation process (A) is initiated by inner-coat adaptor protein-dependent cargo sorting, followed by membrane deformation mediated by clathrin and structural scaffold of COPII subcomplex. Subsequently, scission machinery including dynamin 1 and ESCRT-III catalyzes the membrane fission and dissociates vesicle from the lysosomal membrane. The process of tubulation (B) is best described by autophagic lysosome reformation (ALR), wherein proto-lysosomes derived from ALs, mature into functional lysosomes known as lysosome reformation. These matured lysosomes then subsequently fuse with autophagosomes to form ALs and initiate the cycle of lysosome reformation. The final event of lysosome fission is kiss-and-run (C), which involves the fusion of lysosomes and late endosomes. The transient interaction (“Kiss”) between lysosome and LEs allows the exchange of content, followed by separation of the lysosome (“Run”).