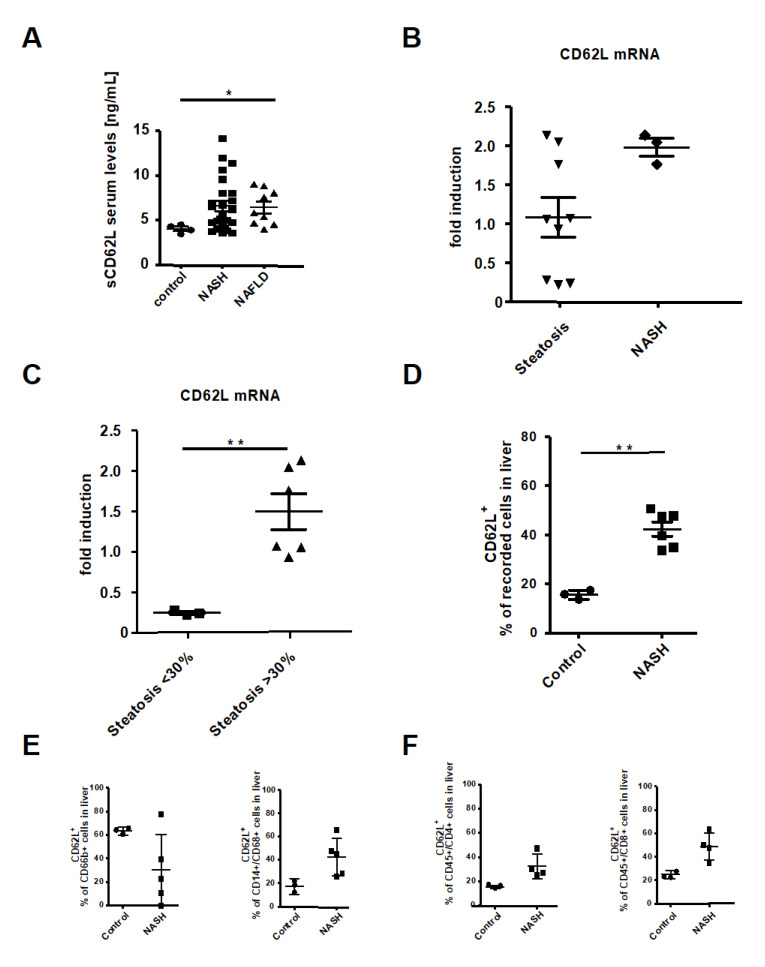
Figure 1.
CD62L (L-Selectin) is increased in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients. (A) Serum levels of soluble L-Selectin were measured via ELISA in depicted patient groups (* p < 0.05). (B) Liver biopsy samples were analysed for CD62L mRNA expression by RT-qPCR. The values were expressed as fold induction over the mean values obtained for control patient liver biopsies. (C) Results from (B) were grouped by patients with <30% and <30% steatosis. Values were expressed as fold induction over the mean value obtained for control patient samples (** p < 0.01). (D) Intrahepatic CD62L+ cells were analysed by flow cytometry in depicted patient groups. Cells were gated via, forward scatter/side scatter (FSC/SSC) duplets were excluded, living cells, CD45+/CD62L+. Depicted is the analysis of the percentage of recorded cells (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). (E) Intrahepatic CD62+/CD66b+ neutrophils and CD14+/CD68+/CD62L+ monocytes were analysed by FACS. Analysis included control patients and patients suffering from NASH. Intrahepatic cells were gated by FSC/SSC, duplets were excluded, living cells, CD45+, CD66b+, CD62L or CD14+/CD68+, CD62L+. Displayed is the percentage of CD62L+ cells in liver biopsy samples. (F) Intrahepatic CD4+/CD62L+ and CD8+/CD62L+ T cells were analysed by FACS in control and NASH patients. CD4+/CD62L+ and CD8+/CD62L+ T cells were gated by FSC/SSC, duplets were excluded, living cells, CD45+, CD4+/CD62L+ or CD8+/CD62L+. Results are displayed as percentage of CD62L+ cells (** p < 0.01).