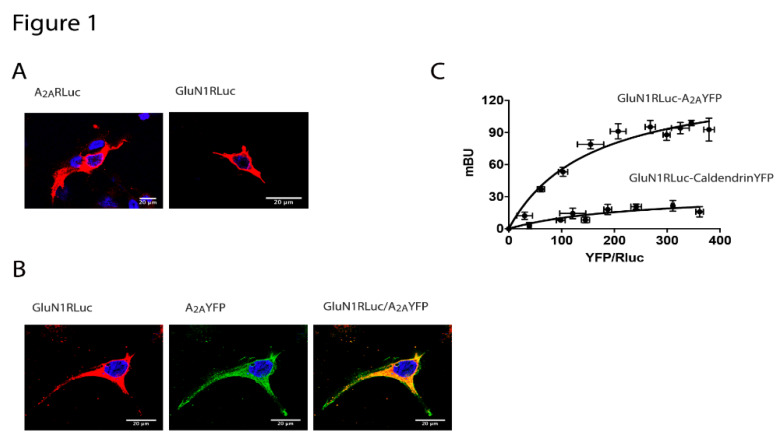
Figure 1.
The N-methyl d-aspartate (NMDA) and the adenosine A2A receptors interact to form heteromeric complexes. In (A,B), HEK-293T cells were transfected with 0.5 μg cDNA corresponding to the A2A receptor (A2AR)-Renilla luciferase (RLuc) (A left) or 0.5 μg cDNA corresponding to the GluN1-RLuc in the presence of 0.3 μg cDNA corresponding to GluN2 (A right) or co-transfected with 0.4 μg cDNA for A2AR-yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) and 0.4 μg cDNA corresponding to the GluN1-RLuc in the presence of 0.25 μg cDNA corresponding to the GluN2 (B). Confocal microscopy images are shown. The receptors fused to RLuc were identified by immunocytochemistry (red) and the proteins fused to YFP were identified by its own fluorescence (green). Colocalization is shown in yellow in the merge image. Scale bar: 20 µm. In (C), the bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) saturation experiments were performed in HEK-293T cells transfected with 0.3 μg of cDNA corresponding to the GluN1-RLuc, 0.2 μg of cDNA corresponding to the GluN2 and increasing amounts of cDNA corresponding to A2AR-YFP (0.1 μg to 0.5 μg) or caldendrin-YFP (0.1 μg to 0.7 μg) as a negative control. The relative amount of BRET is given as a function of 1000× the ratio between the fluorescence of the acceptor (YFP) and the luciferase activity of the donor (RLuc). BRET is expressed as milli BRET units (mBU) and is given as the mean ± SEM of 6 different experiments grouped as a function of the amount of BRET acceptor.