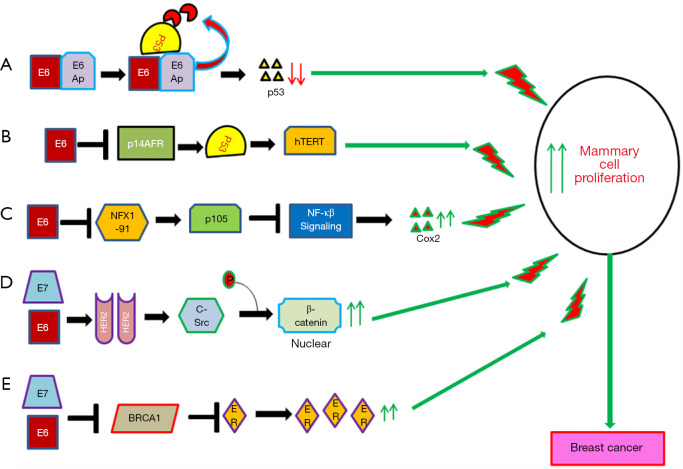
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram represent the Putative mechanism of HPV in breast carcinogenesis. (A) Interaction of E6 with E6-AP leads to the degradation of p53 resulting in increased cellular proliferation eventually transforming into immortalized mammary epithelial cells (MEC). (B) E6 linked with hTERT can mediate immortalization of MEC through inactivation of p14ARF-p53 pathway (V) E6 could increase the mammary cell proliferation through up regulation of Cox2. This occurs due to E6 mediated degradation of NFX1 resulting in p105 down regulation and stabilizing NF-κβ which can now activate transcription of COX2. (D) E6/E7 interaction with HER2 results in its activation. HER2 in-turn activates c-Src which leads to the phoshorylation of beta-catenin at its C-terminal end as a result of which beta-catenin translocates to nucleus and activates different proliferation associated genes. (E) E6/E7 inhibits the function of BRCA1 resulting in restoration of expression of ER. High expression of ER leads to increased proliferation of mammary cell due to modulation of different proliferation associated genes.