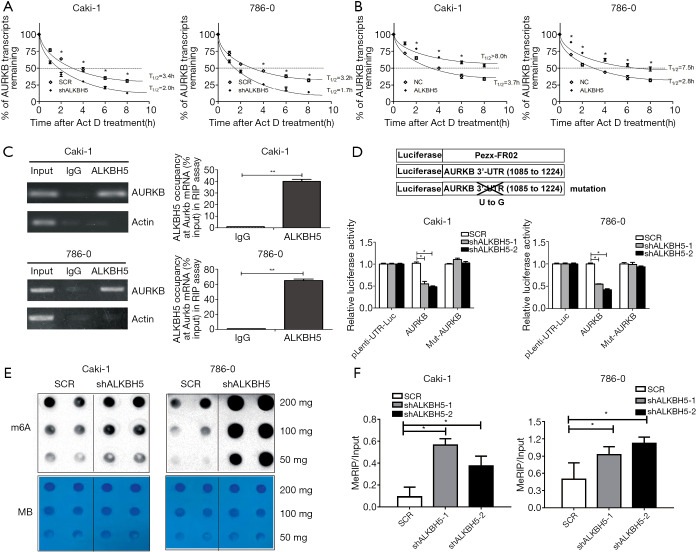
Figure 4.
ALKBH5 enhanced the stability of the AURKB transcript by direct binding to AURKB mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. (A) The half-life of AURKB transcript was decreased after ALKBH5 knockdown. (B) The half-life of AURKB transcript was enhanced by ALKBH5 overexpression. (C) RIP assays showed that ALKBH5 interacted with AURKB mRNAs in 786-0 and Caki-1 cells. The agarose electrophoresis results of the PCR products are shown in the left panel. The qRT-PCR results of RIP assays are shown in the right panel. (D) Relative luciferase activities of the reporter carrying AURKB 3'-UTR with either wild-type or mutation after transfection into ALKBH5-knocked down or the control cells were measured. Relative luciferase activities were normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. (E) m6A-modified RNAs were measured by dot blot using m6A antibody in 786-0 and Caki-1 cells with or without knockdown of ALKBH5. ALKBH5 knockdown resulted in significantly increased m6A levels in a dose-dependent manner. MB, methylene blue (as loading control). (F) MeRIP assays showed that ALKBH5 knockdown caused a significant increase in the m6A levels of AURKB in RCC cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.