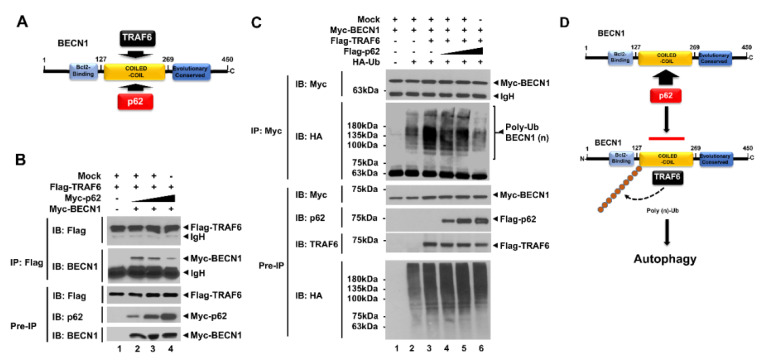
Figure 2.
p62 interrupts the association of TNF (Tumor necrosis factor) receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6)-BECN1 complex and inhibits the ubiquitination of BECN1. (A) TRAF6 and p62 interact with the coiled-coil domain of BECN1. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with mock vector, Flag-tagged TRAF6, and Myc-tagged BECN1, along with different concentrations of Myc-tagged p62, as indicated. Transfected cells were harvested, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and probed with anti-Flag, anti-p62, or anti-BECN1 antibody. (C) HEK293T cells were transfected with mock vector, Myc-tagged BECN1, Flag-tagged TRAF6, and HA-tagged Ub, along with different concentrations of Flag-tagged p62, as indicated. Transfected cells were harvested, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody and probed with anti-Myc, anti-HA, anti-p62, or anti-TRAF6 antibody. (D) A schematic model for how p62 interrupts the association of TRAF6-BECN1 complex and inhibits the ubiquitination of BECN1. TRAF6 interacts with the coiled-coil domain of BECN1 and induces the ubiquitination of BECN1, leading to autophagy activation. Simultaneously, p62 can interact with the coiled-coil domain of BECN1, and that inhibits the interaction of TRAF6 to BECN1 and the ubiquitination of BECN1.