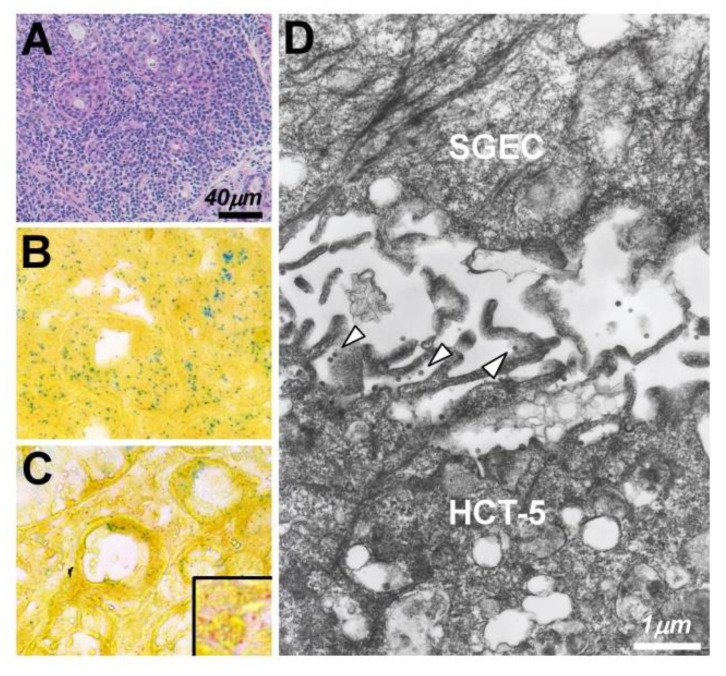
Figure 1.
The expression of tax/HBZ and HTLV-1 virions in salivary glands (SGs) of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome (SS). (A) Massive lymphocytic infiltration was by hematoxylin-eosin staining in a labial salivary gland from a patient with sicca symptoms and adult T-cell leukemia (ATL). The expression of tax/HTLV-1 bZIP factor (HBZ) in SGs from a patient with ATL (B) and patients with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy complicated with SS (C), examined by in situ hybridization. A dominant expression of HBZ (green) was observed in the ATL SGs in both infiltrating mononuclear cells (MNCs) and ducts (B). In contrast, a dominant expression of tax (red) was observed in MNCs of salivary glands from patients with HAM-SS (C). Electron microscopy (D) revealed the existence of HTLV-1 virions (arrowheads) at the contact face between HCT-5 cells (an HTLV-1-infected cell line) and salivary gland epithelial cells (SGECs).