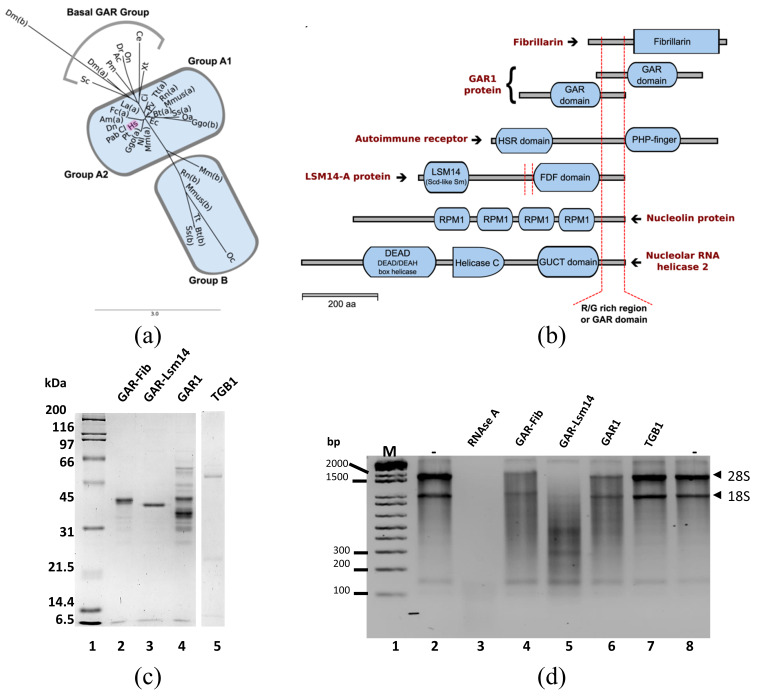
Figure 6.
RNA activity of GAR domains from different RNA-binding proteins. (a) Bioinformatic analysis of R/G rich region (or GAR domain) of retrieved proteins from 36 complete genomes. The phylogenetic tree of GAR domains of fibrillarin proteins was retrieved from chordates genome data. GAR domains were clustered in three major clades: A, B, and the basal group. Clade A was divided into A1 and A2 subgroups. (b) Schematic representation of different modular proteins shows the presence of GAR domains in N- or C-terminal regions. Five proteins contained GAR domains similar to fibrillarin: GAR1 protein, an autoimmune receptor, Lsm14, Nucleolin, and a nucleolar RNA helicase 2. (c) IMAC affinity purification of GAR domains from fibrillarin, Lsm14, GAR1, and viral protein TGB1 with a disordered domain similar to GAR. (d) In vitro RNA assay of four GAR domains expressed and purified from E. coli. TGB1 and GAR1 (Lanes 6 and 7) showed no activity against total RNA. RNAse A diluted 1:20,000 was used as control.