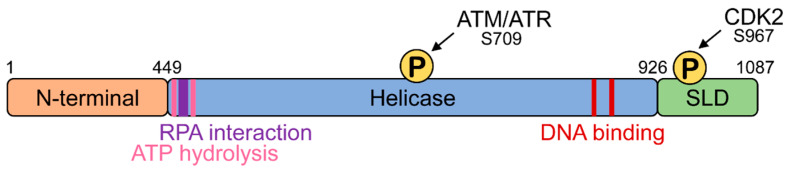
Figure 1.
HELB domain structure. HELB has a N-terminal domain, a helicase domain that binds DNA [6], hydrolyzes ATP [2], and interacts with RPA [7], and a subcellular localization domain (SLD) [7]. The SLD is phosphorylated by CDK2 at the G1 to S transition [7] and the helicase domain is phosphorylated in response to ionizing radiation [12]. Note that the boundary between the N-terminal domain and helicase domain here is different than originally reported [2] due to the discovery of the Q-motif N-terminal to the first helicase motif identified at the time of the original report [9,13].