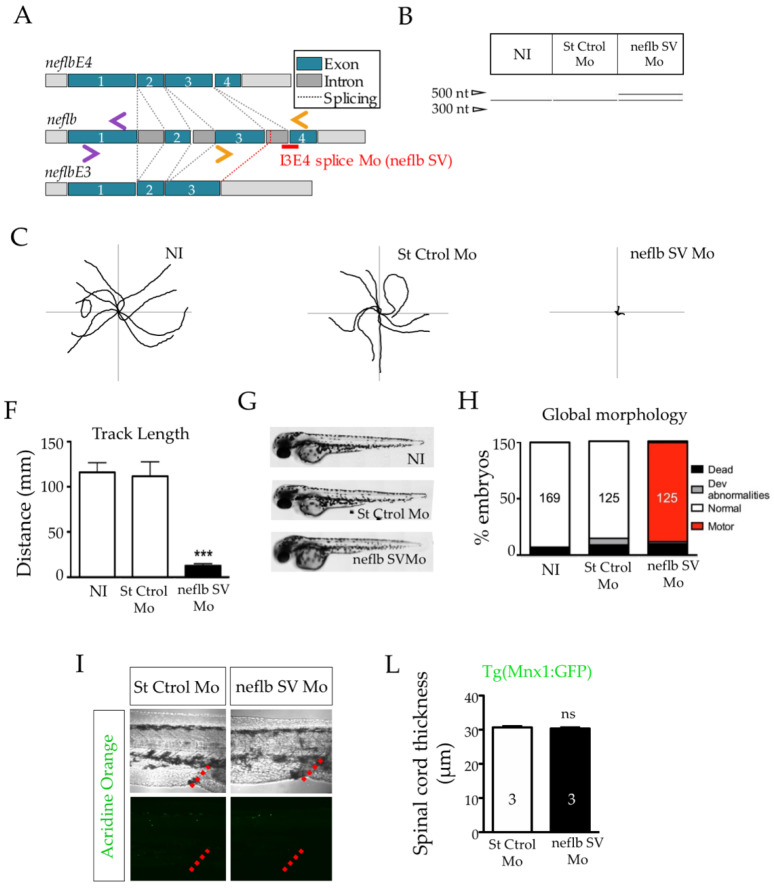
Figure 2.
neflbE3/E4 misbalance results in a strong and specific motor phenotype. (A), position of the splicing variant (SV) antisense oligomorpholino (neflb SV Mo, in red) targeting the decisive I3E4 splice junction in order to inhibit the developmental shift from neflb3E to neflb4E, and of the primer pairs used in this study: ZF Neflb (purple pair) and ZF Neflb SV (orange pair). (B), St Ctrol Mo and neflb SV Mo were injected at the dose of 0.2 mM. The I3E4 morpholino was efficient and caused the persistence of the neflb3E (upper band) expression at 48 hpf, when only neflb4E (lower band) was expressed in controls at this stage. (C), trajectories of 9 representative zebrafish embryos per condition during the touch-evoked escape response at 48 hpf. Non-injected (NI) and control injected embryos (St Ctrol) swam to the edges of a Petri dish in reaction to a light touch; neflb SV morphants were unable to move away from the center of the dish. (F), quantification of the track length shows a reduction by 90% in the swimming distance in neflb SV Mo-injected fish compared with the controls. (G), neflb SV Mo-injected embryos develop without any major developmental abnormality. (H), bar graph of the phenotype distribution after the TEER analysis at 48 hpf. Percentages of zebrafish with motor deficits (motor) are increased after the neflb SV Mo injection. Percentages of normally developed embryos in NI and St Ctrl Mo conditions are comparable. (I), Acridine orange staining (green), which is a metachromatic intercalator sensitive to DNA conformation, is used in this study to detect apoptosis. No higher amount of acridine orange-positive cells was detected in the spinal cord of the neflb SV morphants (right panel) compared with the controls (left panel). The urogenital opening (red dotted lines) has been used as a geographical reference for the measures. (L), spinal cord thickness measured at 48 hpf. *** p < 0.001; ns, non-significant.