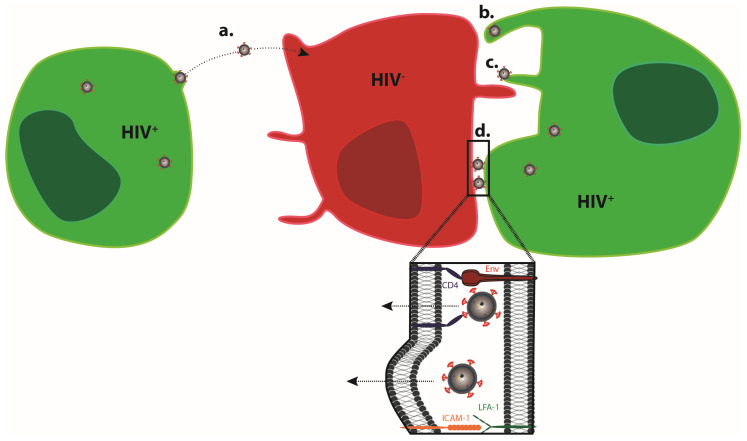
Figure 1.
Transmission modes of HIV-1. Viral particles infect target cells via cell-free (a) or cell-associated (b-d) modes of transmission. (a) Viral particles bud at the surface of infected donor cells, mature, diffuse, and infect non-adjacent target cells. (b,c) Virions can bud at the tip (b) and surf along (c) filopodia to enter in adjacent target cells. In addition, infected and non-infected cells establish close contact, forming a virological synapse (d). Whether HIV-1 enters the target cell via fusion at the plasma membrane or following prior internalization [30,31] remains a matter of debate, and may depend on the nature of the target cell (reviewed in Reference [32]).