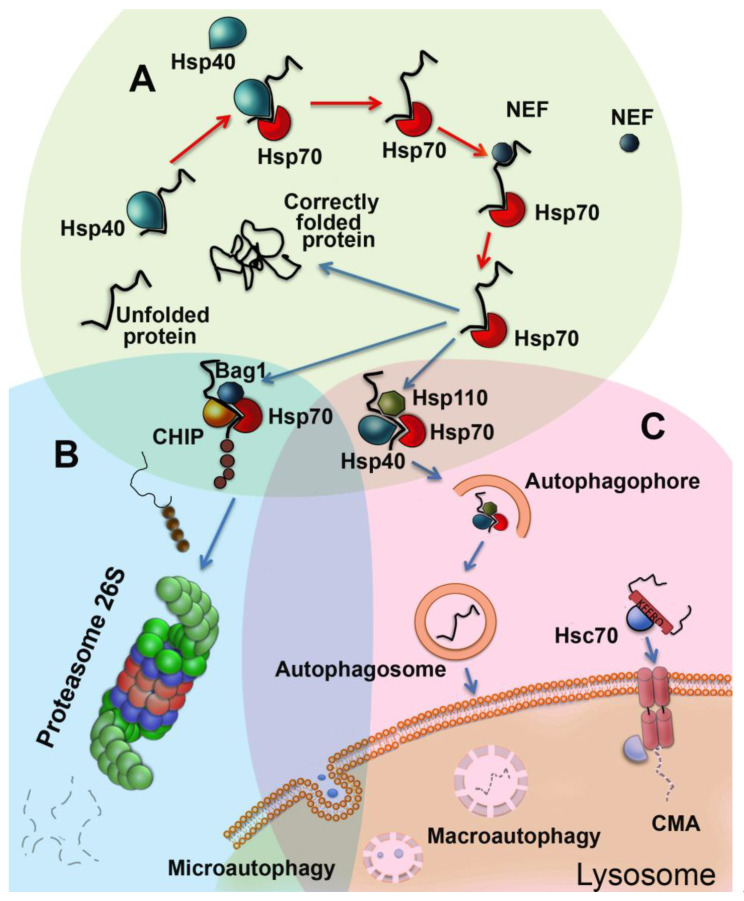
Figure 1.
Proteostasis pathways acting in eukaryotic cells in brief. (A) Chaperonic machinery based on Hsp70 family members includes, besides Hsp70 itself, Hsp40-like (DNAJ family) proteins and nucleotide exchange factors (NEF, Bag domain-containing, Hsp110). In a chaperonic cycle, Hsp40 exposes a molecule of a newly-synthesized or damaged polypeptide to Hsp70 and concomitantly enhances its ATP-ase activity. Corrected substrate protein is released due to the conversion of Hsp70 molecule from ADP to ATP-bound form, performed with the aid of NEFs. If the substrate is incorrigible it is targeted via Bag-1-mediated recruitment of E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP for further proteasomal degradation. The Hsp70-Hsp110-Hsp40 complex may also target improperly-structured polypeptides to maturating autophagosomes. (B) In the UPS cycle, 26S proteasome obtains and cleaves polyubiquitinated proteins by a variety of ubiquitin ligases, resulting in the production of short peptides (see Figure 2 for further details). (C) Autophagy features at least three distinct protein degradation systems, including macroautophagy, which serves for digestion of polypeptides and organelles, microautophagy necessary for the degradation of useless membranous structures, and chaperone-assisted autophagy which targets KFERQ motif-exposing proteins. All types of autophagy possess powerful hydrolytic activity digesting substrates down to amino-acid and supplying cells with nutrients.