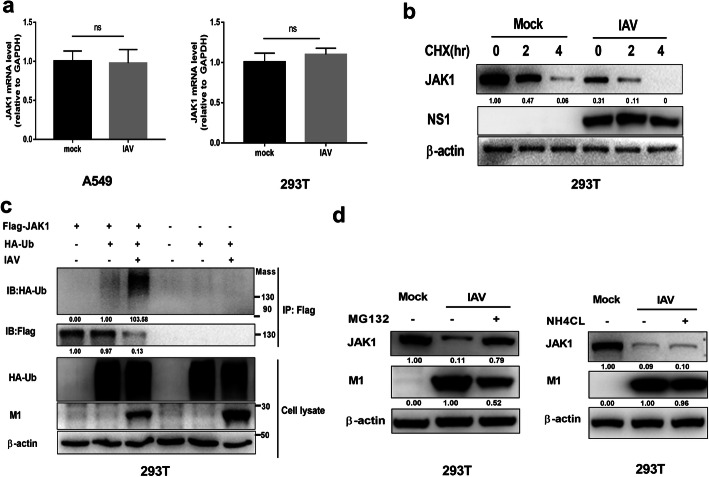
Fig. 2.
IAV infection induces ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of JAK1. (a) 293 T cells and A549 cells were left uninfected or infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. The relative mRNA levels of JAK1 were analyzed by real-time qPCR at 24 hpi. Date are means plus standard deviation for triplicate samples. The experiments were independently repeated twice with similar result. Ns, not significant. (b) 293 T cells were uninfected or infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. At 12 hpi, the cells were treated with solvent or cycloheximide (CHX, 50 μg/ml) for the indicated times. The levels of JAK1, viral NS1 and β-actin were analyzed using Western blotting. (c) 293 T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged JAK1 and HA-tagged ubiquitin, 24 h post transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with IAV at an MOI of 1 as indicated for additional 18 h. Cell lysis was subjected to IP and Western blotting. The ubiquitination of immunoprecipitated Flag-JAK1 was analyzed by Western blotting using anti-HA tag antibody. The protein levels of Flag-JAK1, HA-Ub, β-actin, and viral M1 in the whole-cell lysates were also analyzed using Western blotting. (d) 293 T cells were infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. At 18 h post infection, cells were treated with indicated inhibitors or solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]) for an additional 6 h. The protein levels of JAK1, viral M1, and β-actin were analyzed using Western blotting