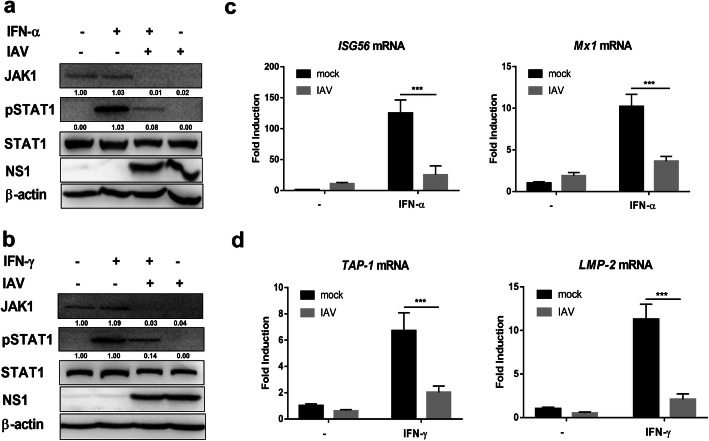
Fig. 3.
IAV infection reduces responsiveness to IFNs. (a) 293 T cells were left uninfected (Mock) or infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. 24 h post infection, cells were left untreated (−) or treated with human IFN-α (1000 U/ml) for 1 h. The levels of JAK1, pSTAT1, STAT1, viral NS1, and β-actin were detected using Western blotting. (b) 293 T cells were left uninfected (Mock) or infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. At 24 hpi, cells were left untreated (−) or treated with human IFN-γ (1000 U/ml) for 1 h. The levels of JAK1, pSTAT1, STAT1, viral NS1, and β-actin were detected using Western blotting. (c) 293 T cells were left uninfected (Mock) or infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. At 24 hpi, cells were left untreated (−) or treated with human IFN-α (1000 U/ml) for 24 h. The relative mRNA levels of Mx1 and ISG56 were analyzed using real-time qPCR. The error bars represent the means plus standard deviations for three independent experiments. ***, P < .0001. (d) 293 T cells were left uninfected (Mock) or infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. At 24 hpi, cells were left untreated (−) or treated with IFN-γ (1000 U/ml) for 6 h. The relative mRNA levels of TAP-1 and LMP-2 were analyzed using real-time qPCR. The error bars represent the means plus standard deviations for three independent experiments. ***, P < .0001