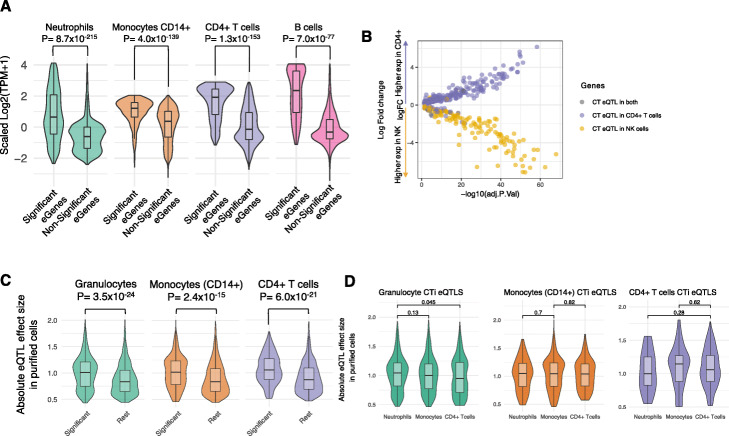
Fig. 4.
Validation of CTi eQTLs. a The expression of CTi eQTL genes in purified cell subpopulations from BLUEPRINT [23] are significantly higher in the relevant cell subpopulation when compared to other available cell subtypes (green for granulocyte eQTL genes showing expression for purified neutrophils; orange for monocytes; purple for CD4+ T cells; pink for B cells). b Genes differentially expressed (Adjusted p-value ≤0.5) between CD4+ T cells and NK cells are significantly enriched for CT eQTLs effects on CD4+ T cells (dots in purple, Fisher exact P = 1.8 × 1017) and NK Cells (dots in yellow, Fisher exact P = 2.3 × 1018), respectively. c CTi-eQTLs (FDR ≤ 0.05) show significantly larger effect sizes in the purified cell eQTL data [9] compared to the rest of the whole blood eQTLs for which we do not detect a cell type effect, as shown for deconvoluted granulocyte eQTLs in neutrophil-derived eQTLs (green),monocytes (orange) and CD4+ T cells (purple)