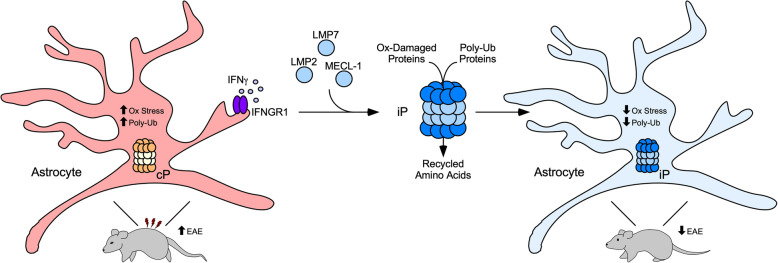
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of the proposed IFNγ-iP axis active in astrocytes during chronic EAE. During MS and EAE, oxidative stress occurs in astrocytes leading to rapid accumulation of oxidatively damaged proteins, which are tagged for degradation by the iP via poly-ubiquitin chains. IFNGR1 signaling in astrocytes leads to the conversion of the constitutive proteasome (cP) to the iP, which more efficiently reduces oxidative stress and removes poly-ubiquitinated proteins, leading to a reduction in lesion size and improved EAE clinical score