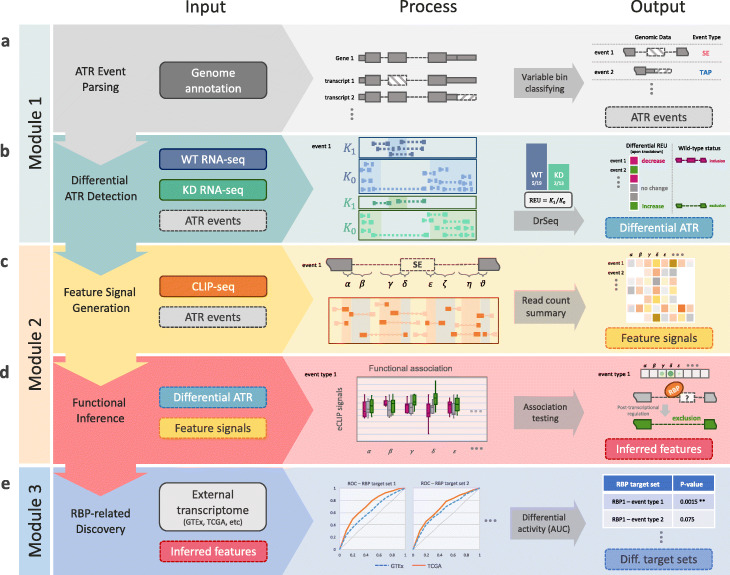
Fig. 2.
Schematic overview of SURF pipeline. a In the analysis module 1, the first step parses alternative transcriptional regulation (ATR) events from genome annotation. b SURF quantifies relative event/exon usage (REU) using RNA-seq data following RBP knockdown (with wild-type control) and performs differential REU analysis (DrSeq). As a result, it infers regulation effects of RBPs as phenotypical labels for each differential ATR event. c In the analysis module 2, SURF extracts location features for each ATR event and generates the feature signals using the complementary eCLIP-seq data. d Then, SURF models differential ATR labels by associating them with the feature signals and infers global positional preferences of RBPs. e In the discovery module, the inferred location features play a key role in downstream RBP-related discovery. The rank-based analysis of RBP transcript targets using external transcriptome datasets (e.g., TCGA and GTEx) discovers differential transcriptional activity through specific RBP and ATR event types