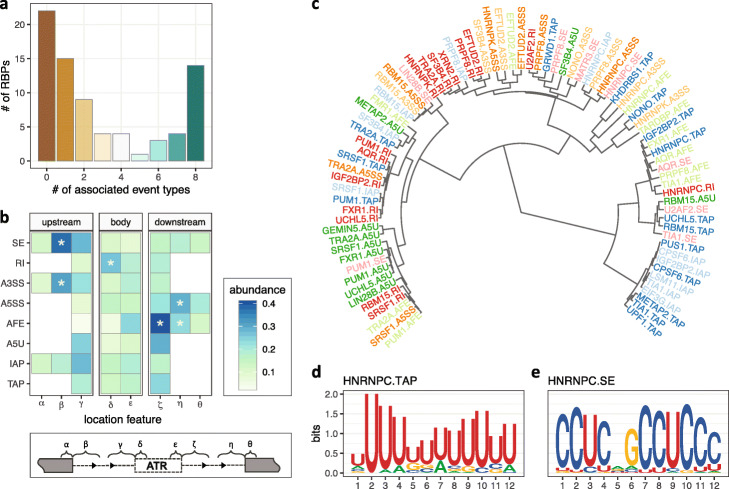
Fig. 5.
Summary of global positioning preferences across 76 RBPs and event-specific sequence preferences of RBPs. a The number of ATR event types that each RBP regulates, summarized from SURF (analysis module 2) results of 76 RBPs. b Aggregation of global positioning association results across each ATR event type. Column strips cluster location features into three groups: upstream, body, and downstream. The darker color indicates higher abundance of RBPs on the location feature (i.e., there are more RBPs for which the specific protein binding associates with differential ATR). Location features with a significant relative abundance at the significance level of 0.05 are marked with an asterisk. c Hierarchical clustering of motifs from de novo sequence analysis of location features for 82 RBP-event type combinations. Each tip point corresponds to the top motif found in SURF-identified location features that associated with a specific combination of RBP and ATR event. Going from the outer tips towards the root, the motifs that merge earlier have higher similarity. d Sequence motif identified in 394 SURF-inferred location features for HNRNPC in TAP (E value 3.0×10−68). The total height of the letters depicts the information content of the position, in bits. e Sequence motif identified in 306 SURF-inferred location features for HNRNPC in SE (E-value 3.2×10−152)