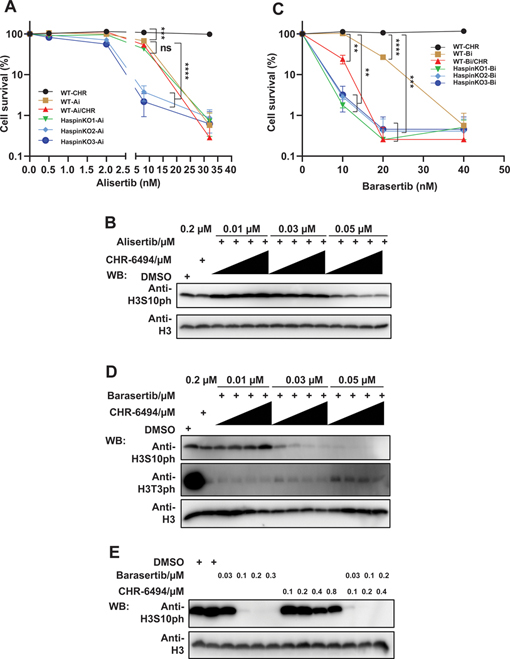
Figure 3.
Haspin inhibitor potentiates the efficacy of AURKB inhibitor but not AURKA inhibitor. (A) Depletion or inhibition of Haspin has no effect on cellular sensitivity to alisertib. HCT116 wild-type (WT) or Haspin knockout (KO) cells were treated with CHR-6494 (CHR; 0, 40, 80, 120, or 160 nM) and alisertib (Ai; 0, 0.5, 2, 8, or 32 nM) and further cultured for 9 days followed by fixation and staining. Experiments were performed in triplicate with duplicate biological replicates. Representative results are shown. Student t tests were performed to estimate differences between 2 groups; ns, not significant; *** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001. (B) Addition of CHR-6494 has no effect on H3S10ph reduction by alisertib. HCT116 cells were plated in 24-well plate overnight and treated with alisertib, CHR-6494, or the combination of CHR-6494 (0.05, 0.1, 0.15, and 0.2 μM) and alisertib for 24 h. Then cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting using indicated antibodies. (C) CHR-6494 potentiates the inhibitory effect of barasertib. Cells treated with barasertib (Bi; 0, 10, 20, or 40 nM) or CHR-6494 (CHR; 0, 40, 80, 120, or 160 nM) were grown for 9 days followed by fixation and staining. Experiments were performed in triplicate with duplicate biological replicates. Representative results were shown. Student t tests were performed to estimate differences between 2 groups; error bar represents SE (n = 3); ** P < 0.01;*** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001. (D) Combination of CHR-6494 and barasertib dramatically reduces the level of H3S10ph. Cells were treated with barasertib or CHR-6494 for 24 h, in combination (Bi combined with 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, and 0.2 μM CHR) or alone (CHR; Bi), and followed by lysis with SDS loading buffer. The samples were then examined by immunoblots with indicated antibodies. H3 was included as loading control. (E) Cells were cultured with barasertib or CHR-6494 for 24 h and then analyzed by Western blotting using indicated antibodies.