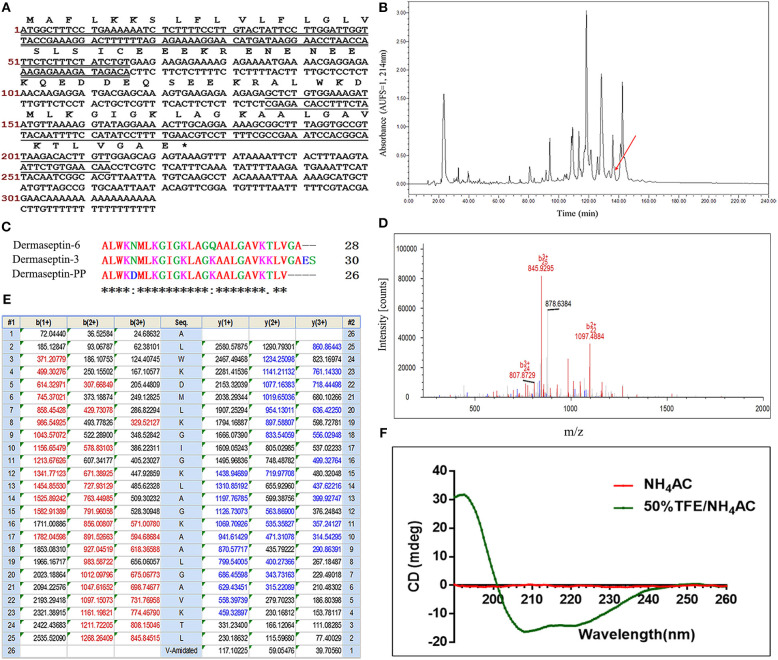
Figure 1.
(A) Nucleotide sequence of cDNA cloned from Phyllomedusa palliata skin secretion and the corresponding translated amino acid sequence of the open reading frame of Dermaseptin-PP precursor. The putative signal peptide is double-underlined; the mature peptide is single-underlined; the termination codon is marked by an asterisk. (B) RP-HPLC chromatogram of P. palliata skin secretion at a wavelength of 214 nm with a flow rate of 1 mL/min in 240 min. The retention time (at 136.5 min) of Dermaseptin-PP is indicated by an arrow. (C) Alignment of cDNA deduced mature Dermaseptin-PP sequence with the top 2 non-repetitive similar dermaseptin peptide sequences from BLAST analysis. An “*” represents conserved residues; a “:” represents very similar residues and a “.” indicates similar residues. (D) Annotated LCQ tandem mass (MS/MS) fragmentation spectrum of Dermaseptin-PP. (E) Predicted single-, double-, and triple-charged b- and y-ion series arising from LCQ MS/MS fragmentation of Dermaseptin-PP. The actually observed fragment ions following actual fragmentation are severally colored red (b-ions) and blue (y-ions). (F) The circular dichroism (CD) spectra of pure Dermaseptin-PP in 10 mM ammonium acetate (NH4Ac) water solution (red line) and 50% 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (TFE)-10 mM NH4Ac water solution (green line).