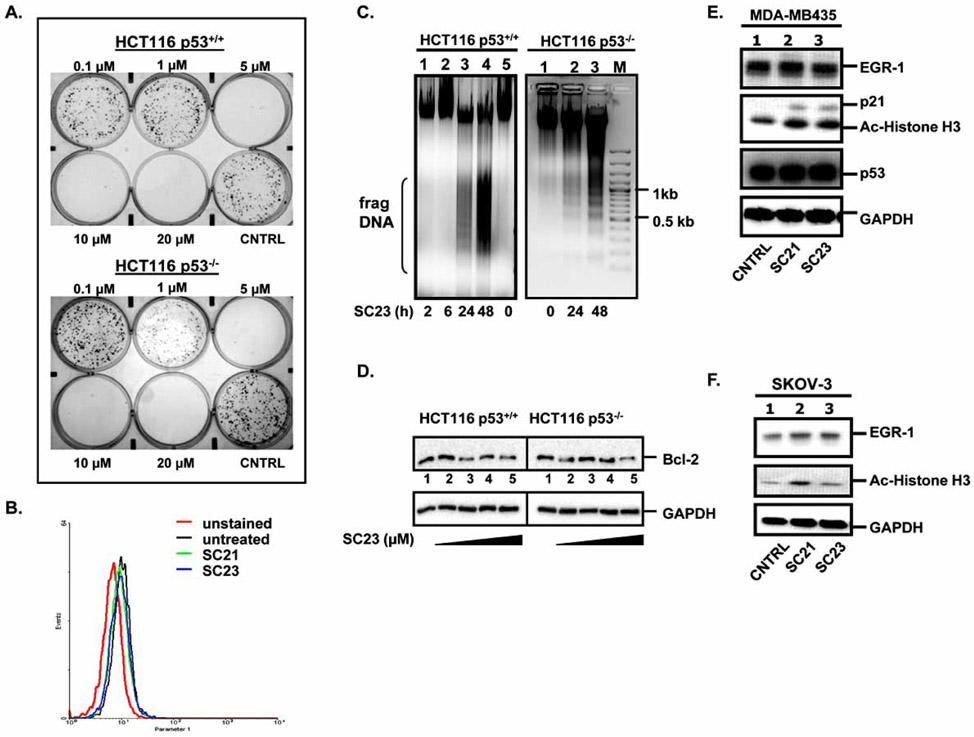
Fig. 3. SC23 triggers apoptosis in HCT116 p53+/+ and HCT116 p53−/− cells.
(A). SC23 exhibits cytotoxicity in the tested cell lines as shown by colony formation assay. (B). Detection of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in SKOV-3 cells. SKOV-3 cells were treated with SC21 and SC23 for 24 h. The untreated and treated cells were incubated with MitoSOX, trypsinized, washed with Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution, and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. (C). SC23 causes DNA fragmentation in both HCT116 p53+/+ and HCT116 p53−/− cells. Cells were treated with 5 μM of SC23 for the indicated duration. Cells were then lysed with lysis buffer. Precipitated DNA was resuspended in TE buffer and digested with RNase A and the digested product was separated on 1 % agarose gel. (D). SC23 decreases the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein levels in both cell lines. HCT116 p53+/+ and HCT116 p53−/− cells were treated with increasing concentrations of SC23 for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were extracted and equal amounts of total protein were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE. The proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Bcl-2 antibodies. (E). SC21 and SC23 up-regulate the expressions of p21 and acetylated histone H3 in MDA-MD-435 cells. Cells were treated with SC21 and SC23 for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting analysis with the appropriate antibodies. (F). SC21 and SC23 up-regulate acetylated histone H3 in SKOV-3 cells. Cells were treated with SC21 and SC23 for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were analyzed with Western blotting with the appropriate antibodies.