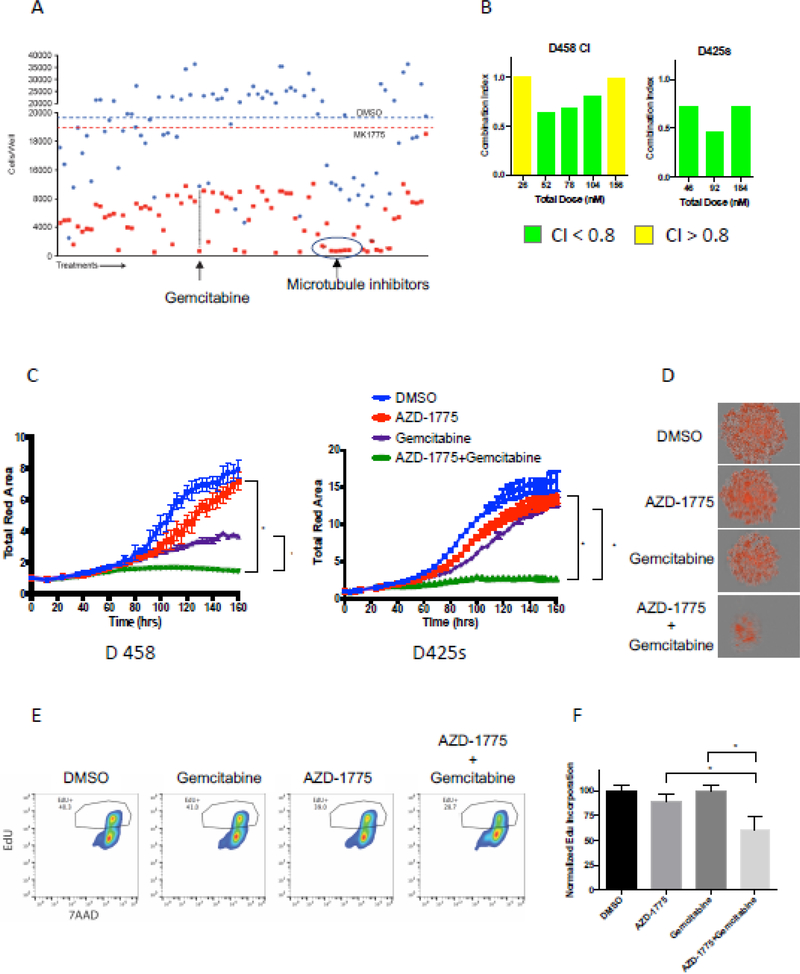
Figure 2.
Gemcitabine synergizes with AZD-1775 to enhance cell death of MYC-medulloblastoma cells. A) Treatment of D458 cells with the oncology drug library of 91 FDA- approved oncology drugs at 1μM with and without AZD1775 (75nM, IC25) identified gemcitabine as a drug which synergizes in cell killing with AZD-1775. B) Combination index study showing the concentrations of Gemcitabine that leads to synergistic cell killing in the presence of AZD-1775 in D458 and D425 high-myc cell lines. CI <0.8 indicates synergism between the two drug treatments. C) Synergistic effect of the two drugs AZD-1775 and Gemcitabine treatment on inhibiting the ability of Myc-MB cells to form neurospheres. D) Representative pictures of neurospheres formed at the end of 7day treatment with either drugs alone or in combination with the combination of drugs showing significant decrease in neurosphere size. E) Representative histogram of flow cytometry assay using anti-EdU (FITC)/7AAD to measure cell proliferation. The combination of AZD-1775 and Gemcitabine significantly decreased EdU incorporation (10uM) after 24 hours of incubation when compared to either drug alone in D458 and D425S cells thereby suggesting an effective decrease in cell proliferation. F) Quantitation of cell-incorporated EdU to total DNA content.