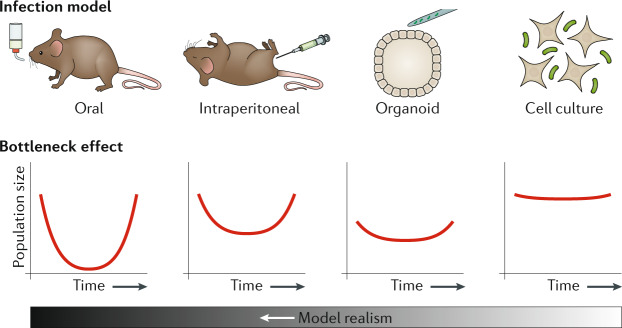
Fig. 5. Bottleneck and realism trade-off in TIS infection models.
Different animal models of infection (top) can induce strong bottleneck effects (bottom) in infecting bacterial populations, which can confound transposon-insertion sequencing (TIS) analysis. This bottleneck effect is particularly pronounced in models where bacteria must overcome barrier defences (for example oral infection models of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium). Organoid models can provide a complex environment while limiting bottlenecks, but technical limitations in culture may limit the total population size screened. Finally, cell culture screens can be scaled to arbitrary sizes, allowing screening of extremely large collections of mutants, but they often provide insight into only a particular aspect of disease.