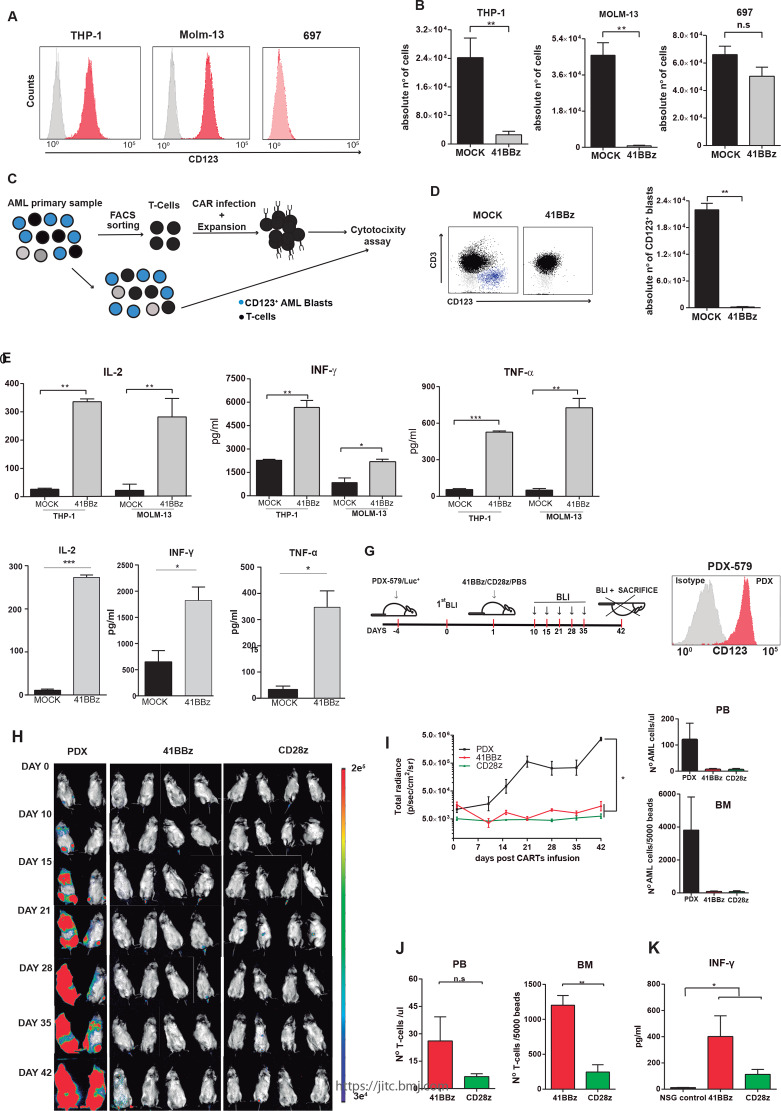
Figure 2.
41BB-CD123 CARTs specifically target and eliminate CD123+ AML cells in vitro and in vivo. (A) Surface expression of CD123 (red) in THP-1, MOLM-13 and 697 cell lines. (B) Absolute counts of alive residual target cells measured by FACS in 48-hour cytotoxicity assays at 1:1 E:T ratio (n=3). Data are presented as mean±SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (C) Graphical cartoon of the experimental design for autologous cytotoxic assays. Normal CD3+ T-cells were FACS-purified from the BM of patients with AML (n=3), infected with CD123 CAR, expanded, and exposed to autologous total PBMCs (1:1 E:T). Residual CD123+ blasts were quantified 48 hours post-41BB-CD123 CART exposure. (D) Left: representative FACS analysis of the cytotoxicity assay. T-cells are shown in black and CD123+ blasts in blue. Right: absolute counts of alive AML blasts in 48-hour cytotoxicity assays at 1:1 E:T ratio (n=3). (E, F) ELISA showing robust secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by 41BB-CD123 CARTs after exposure to CD123+ cell lines (E) and AML primary blasts (F) for 16 hours at 1:2 E:T ratio (n=3). (G) Experimental design to assess in vivo the efficacy of both 41BB-based and CD28-based CD123 CAR. NSG mice were intravenously injected with 2.5×105 Luc-expressing xenograft AML cells (PDX-579) followed 5 days after by a single intravenous injection of 3×106 CD123 CARTs (either 41BB or CD28) generated from healthy PBMCs. Tumor burden was monitored every 7–10 days by BLI using IVIS imaging. (H) IVIS imaging of tumor burden monitored by BLI at the indicated time points. (I) Left: total radiance quantification (p/s/cm2/sr) at the indicated time points for 41BB-CD123 CARTs, CD28-CD123 CARTs and untreated mice. *P<0.05. Right: absolute counts of residual AML cells in PB and BM at endpoint. (J) T-cell persistence in PB and BM at endpoint. (K) In vivo quantification by ELISA of IFN-γ in PB sera collected in the acute phase (10 days post-CART infusion). *p<0.05. AML, acute myeloid leukemia; BLI, bioluminescence; BM, bone marrow; CART, chimeric antigen receptor Tcell; E:T, effector:target; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IVIS, in vivo imaging system; ns, non-significant; NSG, non-obese diabetic-Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ; PB, peripheral blood; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell.